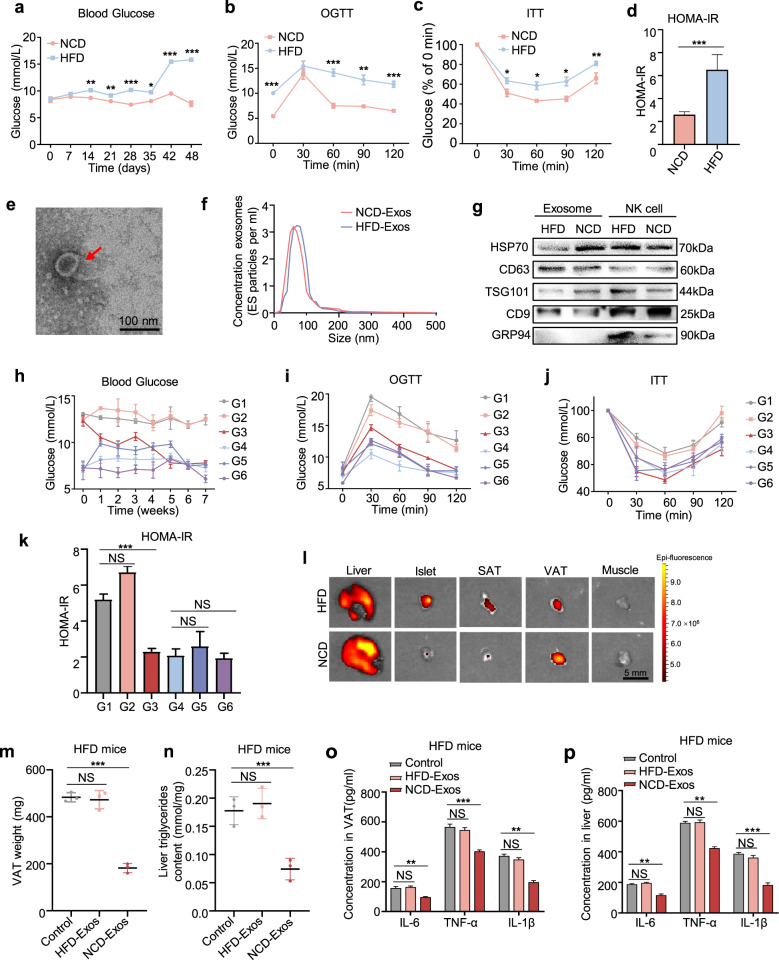
Fig. 1.
NK-derived exosomes from lean mice attenuate obesity-induced insulin resistance. a Fasting blood glucose of NCD and HFD mice after group feeding. b–d OGTT (b), ITT (c), and HOMA-IR index (d) of HFD mice and NCD mice (n = 48) were recorded at 42 days after group feeding. HOMA-IR = Fasting blood glucose value × fasting serum insulin value/22.5. e Transmission electron micrographs of NK-derived exosomes. Scale bar, 100 nm. f NanoSight particle tracking analysis showing the particle size of NK-derived exosomes isolated from NCD and HFD mice. g Western blot assays of exosomal markers TSG101, HSP70, CD63, and CD9. h–k After blank liposomes, NCD-Exos, and HFD-Exos were separately injected into NCD or HFD mice via tail vein, fasting blood glucose (h), OGTT (i), ITT (j), and HOMA-IR (k) were assessed in each group. G1: HFD mice treated with blank liposomes (n = 3); G2: HFD mice treated with HFD-Exos (n = 3); G3: HFD mice treated with NCD-Exos (n = 3); G4: NCD mice treated with blank liposomes (n = 3); G5: NCD mice treated with HFD-Exos (n = 3); and G6: NCD mice treated with NCD-Exos (n = 3). l After NCD-Exos labeled with PKH26 were transferred into recipient mice, fluorescence images of the liver, islets, SATs, VATs, and skeletal muscles were observed by in vitro imaging system. Scale bar, 5 mm. m The weight of VATs from HFD mice treated with NCD-Exos, HFD-Exos, or blank liposomes. n Liver triglyceride content of HFD mice treated with NCD-Exos, HFD-Exos, or blank liposomes. o, p ELISA assays of IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α expression in VATs and livers of HFD mice treated with NCD-Exos, HFD-Exos, or blank liposomes. Experiments were performed at least in triplicate, and the results are shown as the mean ± s.d. Student’s t-test was used to analyze the data. (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001)