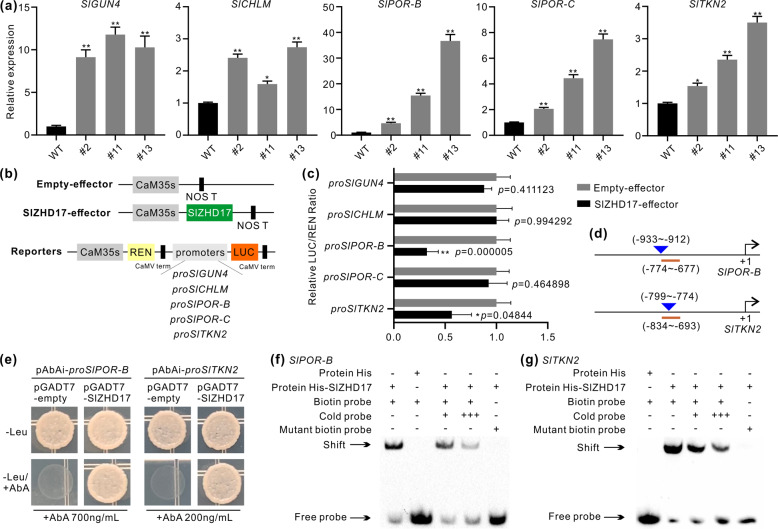
Fig. 4. SlZHD17 directly regulates SlPOR-B and SlTKN2 genes.
a The relative expression levels of SlGUN4, SlCHLM, SlPOR-B, SlPOR-C, and SlTKN2 in WT and SlZHD17-RNAi fruit at the mature green stage. The transcript level in WT was set as 1. Data represent the mean values of three independent experiments, and error bars show the standard error values. Single asterisk (*) and double asterisks (**) refer to significant differences between WT and transgenic lines with P < 0.05 and P < 0.01, respectively (two-tailed Student’s t-test). b Structural schematic diagrams of the effector and reporter plasmids used for the dual-luciferase assay. REN Renilla luciferase, LUC firefly luciferase. c Regulation of the SlGUN4, SlCHLM, SlPOR-B, SlPOR-C, and SlTKN2 gene promoters by SlZHD17 based on dual-luciferase assay. The empty effector was used as a control (set as 1). Data represent the mean values of six independent experiments, and error bars show the standard error values. Single asterisk (*) and double asterisks (**) refer to significant differences between empty effector and SlZHD17-effector with P < 0.05 and P < 0.01, respectively (two-tailed Student’s t-test). The P values are provided in the graph. d Schematic diagrams of sequence positions chosen for yeast one-hybrid assay and electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA). The underlined region indicates the promoter fragment used for the yeast one-hybrid assay, and the triangle indicates the sequence position used for the EMSA. The detailed sequences are provided in Appendix S4. e SlZHD17 binding with SlPOR-B and SlTKN2 promoter fragments assessed by yeast one-hybrid assay. The yeast transformants were cultured on SD/−Leu and SD/−Leu/+AbA media for 3–5 days, and the pGADT7-empty plasmid was used as a control. f, g SlZHD17 binding with SlPOR-B (f) and SlTKN2 (g) promoter regions in vitro by EMSA. TF-His protein incubated with a biotin-labeled DNA probe was used as a negative control. ‘+++’ indicates an increase in the competitor probe; no shift in the band for the His-SlZHD17 protein and mutant biotin-labeled DNA probe further confirmed the specific binding site