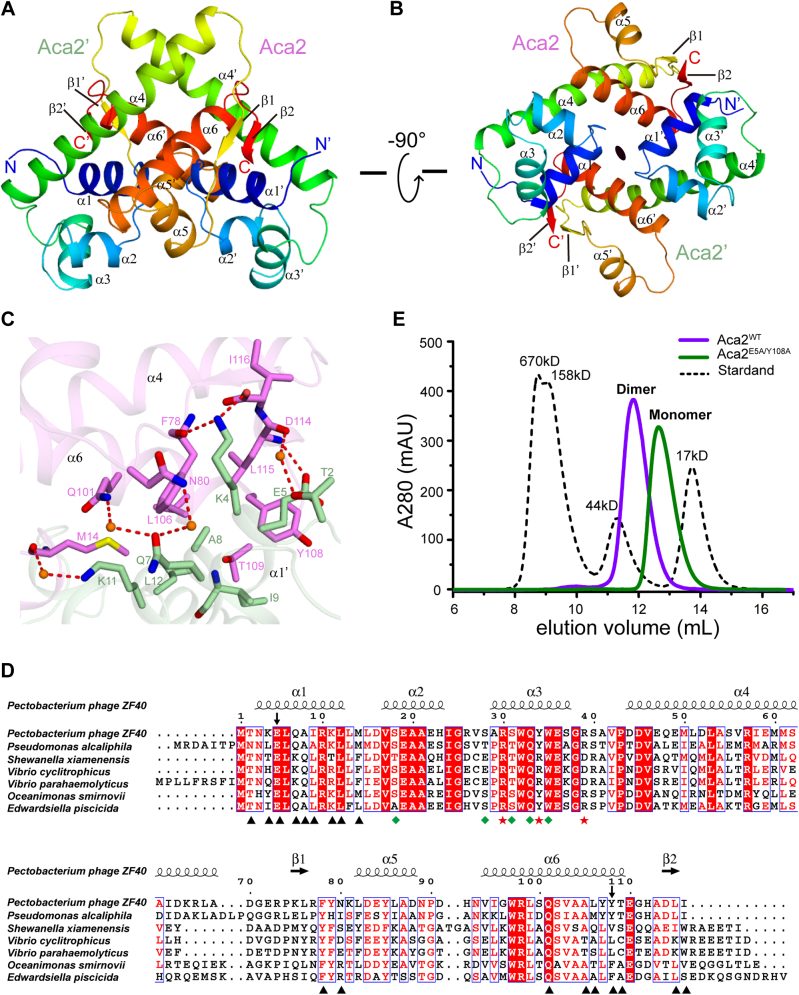
Figure 5.
Structural insight of Aca2 homodimer.A and B, two overall views of the Aca2 homodimer structure 90° apart in the illustration. The two protomers Aca2 and Aca2′ are colored by rainbow from N terminus (blue) to C terminus (red), respectively. C, intermolecular contacts of the Aca2 homodimer. The two protomers Aca2 and Aca2′ are colored in violet and pale green, respectively. The residues involved in interactions are shown in sticks representation. Water molecules are shown as bright orange spheres. Direct and water-mediated hydrogen bonds are shown in red dashed lines. D, sequence alignment of Aca2 from different species. Under alignment, the residues involved in dimer formation are indicated with a black triangle, while the residues interact with the DNA backbone and bases are indicated with green rhombus and red star, respectively. Secondary structures of Aca2 from Pectobacterium phage ZF40 are shown on top of the alignment. The two residues Glu5 and Tyr108 selected for the double mutant E5A/Y108A in panel E are indicated with arrows. E, size-exclusion chromatography analysis of the oligomeric statuses of wild-type Aca2 and double mutant E5A/Y108A. The black dashed line is a molecular weight standard.