Figure 5.
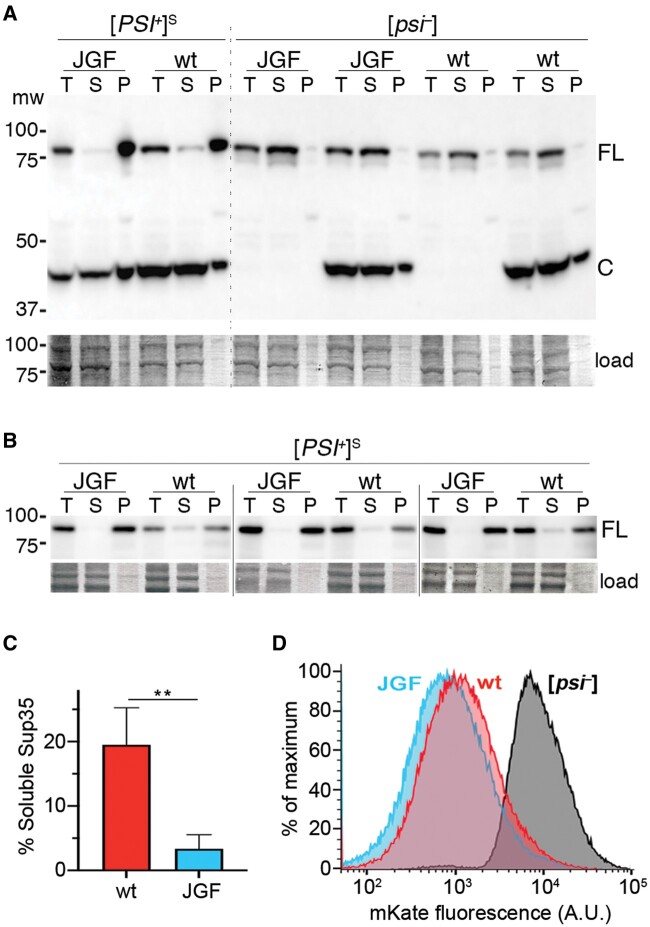
Sup35 is less soluble in cells expressing Sis1JGF in place of Sis1. (A) Shown is an immunoblot of whole lysates (T) of cells expressing Sis1JGF (JGF) or wild-type Sis1 (wt) separated by centrifugation into supernatant (S) and pellet (P) fractions, probed with Sup35 antibody. Cells coexpress Sup35C to ensure viability of Sis1JGF [PSI+]S cells. [psi–] cells, with and without Sup35C, are shown for comparison. The upper band (FL) is full-length Sup35, lower band (C) is Sup35C (amino acids 254–685). The lower panel shows relevant portion of the blotted membrane stained by amido-black as a loading and transfer control. (B) Relevant sections of blots from three additional replicates using [PSI+]S cells and a slightly modified version of the fractionation assay (see Materials and Methods) and yTRAP sensor strain MR1118S. (C) Relative proportions of soluble Sup35 in [PSI+]S cells expressing wild-type Sis1 (19.5 ± 5.8) or Sis1JGF (3.4 ± 2.2) were measured using Image-J. Values are averages of the four [PSI+]S replicates shown; error bars indicate SD (**P < 0.01; t-test). (D) Sup35NM-mKate2 yTRAP sensor was used to monitor Sup35 aggregation in MR1118S (105 live cells) expressing wild-type Sis1 or Sis1JGF. Profile of Sis1JGF [psi–] cells is shown; wild-type Sis1 [psi–] cells were essentially indistinguishable.