FIGURE 1.
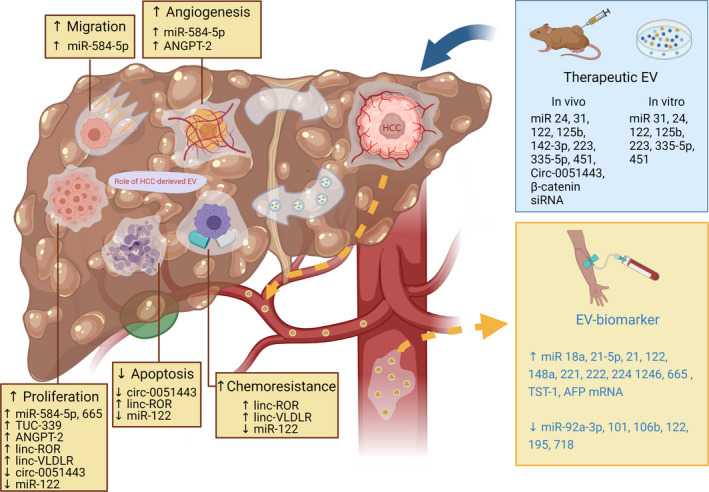
The roles of HCC‐derived EVs, HCC‐derived EVs as a biomarker, and the evidence of therapeutic EVs from currently available reports. HCC cells secrete EVs that can lead to increased tumor cell proliferation, migration, chemoresistance, and decreased tumor cell apoptosis. They can also affect tumor microenvironments such as increased angiogenesis. Some of these HCC‐derived EVs can be detected in circulation, making them available for use as a diagnostic biomarker. Moreover, it is possible for EVs to be used as a therapeutic cargo to transfer therapeutic molecules into tumor cells. Several in vitro and in vivo reports have demonstrated antitumoral effects using this method. miR: microRNA; Circ: circular RNA; siRNA: signal interference RNA; ANGPT2: angiopoietin2; linc: long interceding/intergenic noncoding RNA; TUC: tumor ultraconserved RNA.
