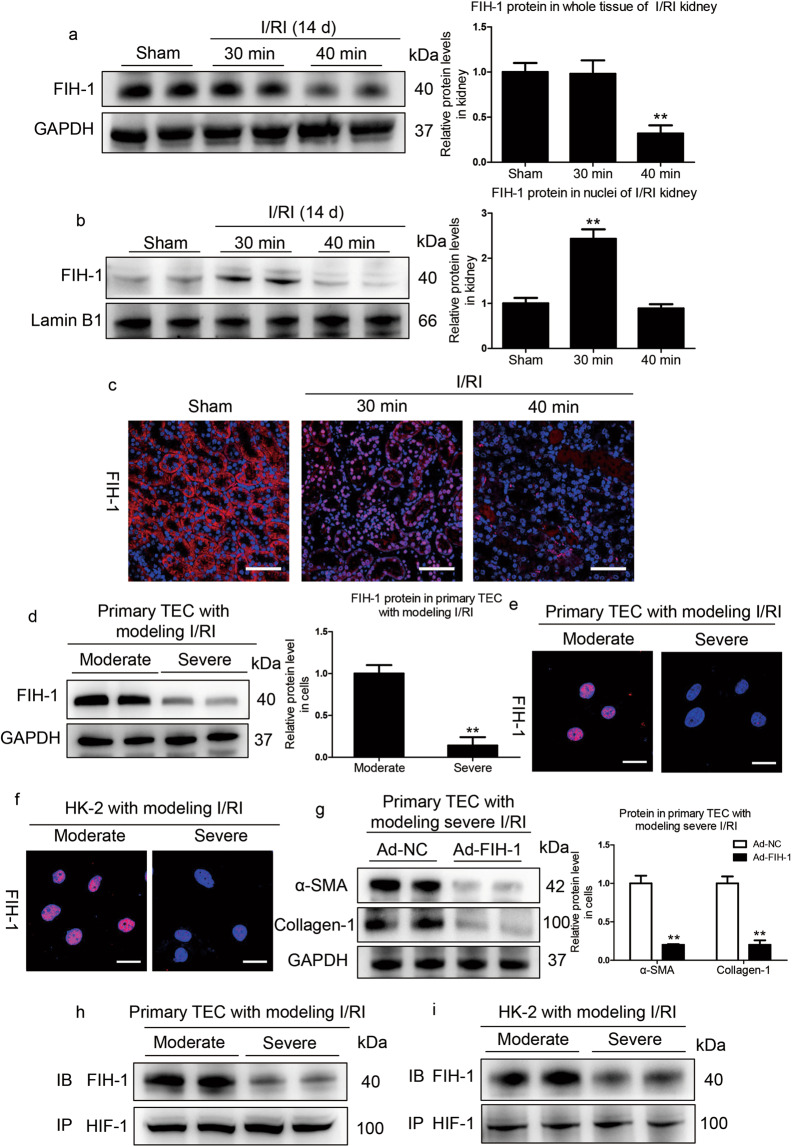
Fig. 7. Decreased tubular FIH-1 mediates the AKI to CKD transition.
a Western blotting analyses of the total protein levels of FIH-1 on day 14 in kidneys of mice subjected to 30 or 40 min of I/RI (n = 7). b Western blotting analyses showing nuclear levels of FIH-1. The quantified expression levels are shown in the right panel (n = 7). The relative expression was normalized to Lamin B1. c Representative results of FIH-1 immunostaining. Scale bars, 50 μm. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of seven mice. **P < 0.01 versus the sham control (Dunnett’s test). D1, day 1; D14, day 14. d Western blotting analyses of FIH-1 expression in primary TECs after simulated moderate or severe I/RI. Data were obtained from three independent experiments. **P < 0.01 compared with cells exposed to simulated moderate I/RI. e Immunofluorescence staining showing FIH-1 expression in primary TECs with different treatments (n = 4). Scale bars, 20 μm. f Immunofluorescence staining showing FIH-1 expression in HK-2 cells with different treatments (n = 4). Scale bars, 20 μm. g FIH-1 was overexpressed using adenovirus (Ad-FIH-1), and α-SMA and collagen-1 expression was analyzed by Western blotting in primary TECs after simulated severe I/RI. The quantified expression levels are shown in the right panel (n = 3). **P < 0.01 compared with cells exposed to Ad-NC (control). h, i Immunoprecipitation (IP) of proteins isolated from cells with an antibody against HIF-1α followed by immunoblotting (IB) analyses with a FIH-1 antibody showed the interaction of HIF-1α and FIH-1 in cells exposed to moderate or severe I/RI. Rabbit IgG served as the control (n = 4).