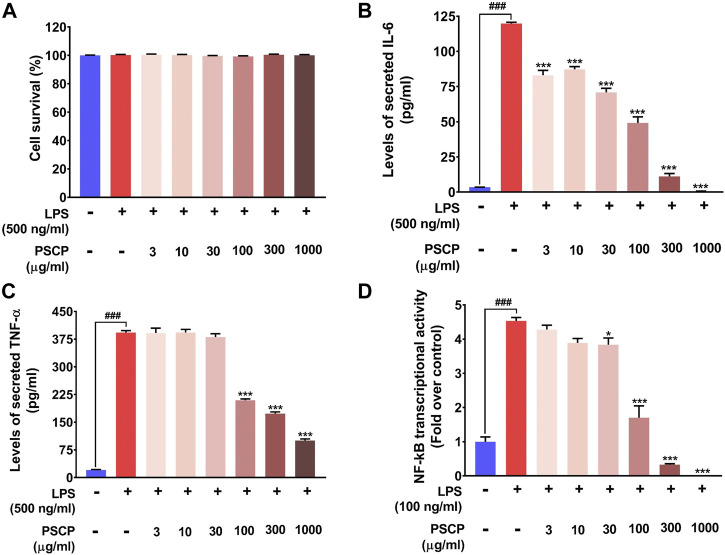
FIGURE 7.
PSCP inhibited pro-inflammatory cytokine release in vitro by modulating NF-κB signaling at cyto-safe doses. (A) Cytotoxicity analysis of different concentrations of PSCP used to treat LPS-induced THP-1 cells demonstrating the suitability of the in vitro inflammatory model for subsequent experiments. (B,C) Quantitative representations of the effects of PSCP treatment on the levels of IL-6 (B) and TNF-α (C) secreted in the cell supernatant by differentiated THP-1 cells in response to LPS-induced inflammation. (D) Effect of PSCP on LPS-induced NF-κB signaling measured through SEAP reporter assay. Data is represented as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was analyzed through one-way ANOVA and represented as ### for p < 0.001, when significantly different from the normal cells, untreated with PSCP and LPS, or as * and *** for p < 0.05 and <0.001, respectively, when the comparison was with the PSCP-untreated LPS-treated group.