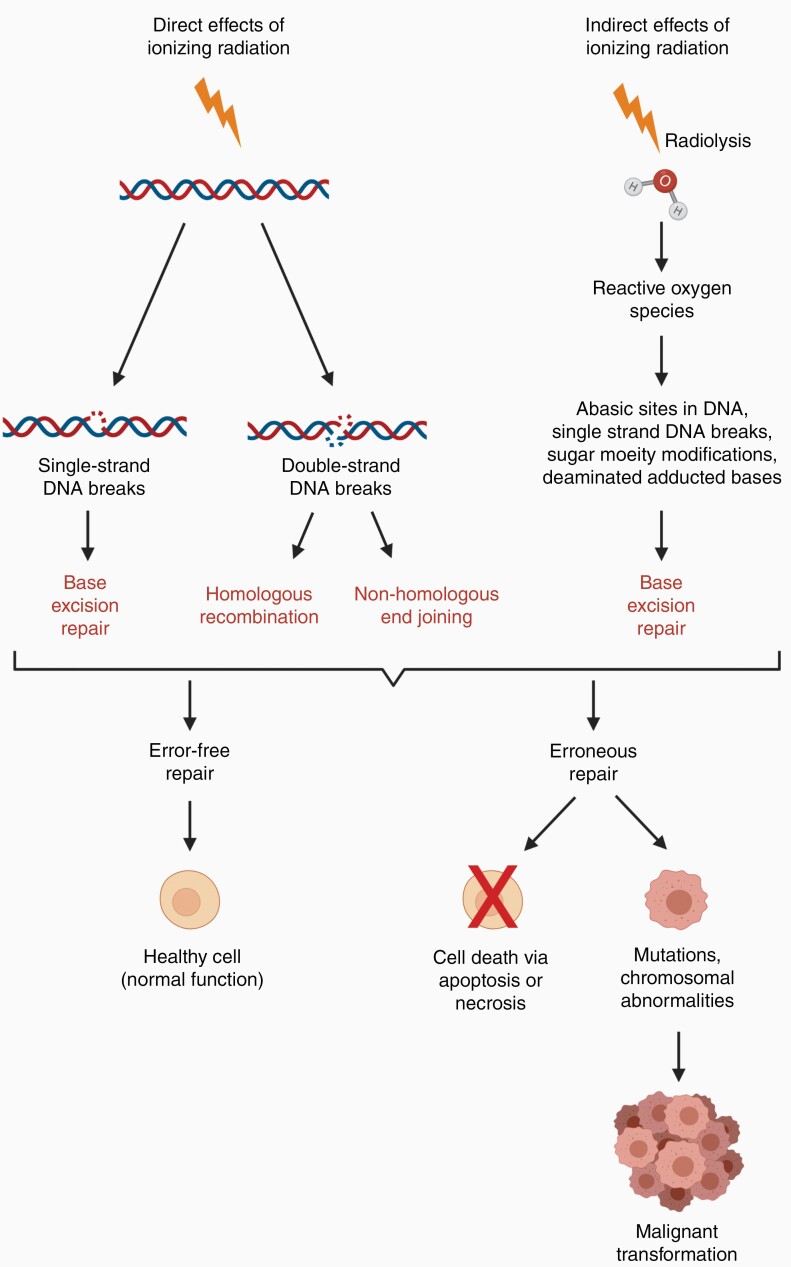
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of DNA damage caused by ionizing radiation. Ionizing radiation damages DNA both directly and indirectly. Depending on the type of damage caused, cells will attempt to repair DNA lesions by base excision repair, homologous recombination or non-homologous end-joining. Successful repair results in a healthy cell with normal function whereas unsuccessful repair may result in cell death or the accumulation of mutations or chromosomal abnormalities, potentially leading to malignant transformation.