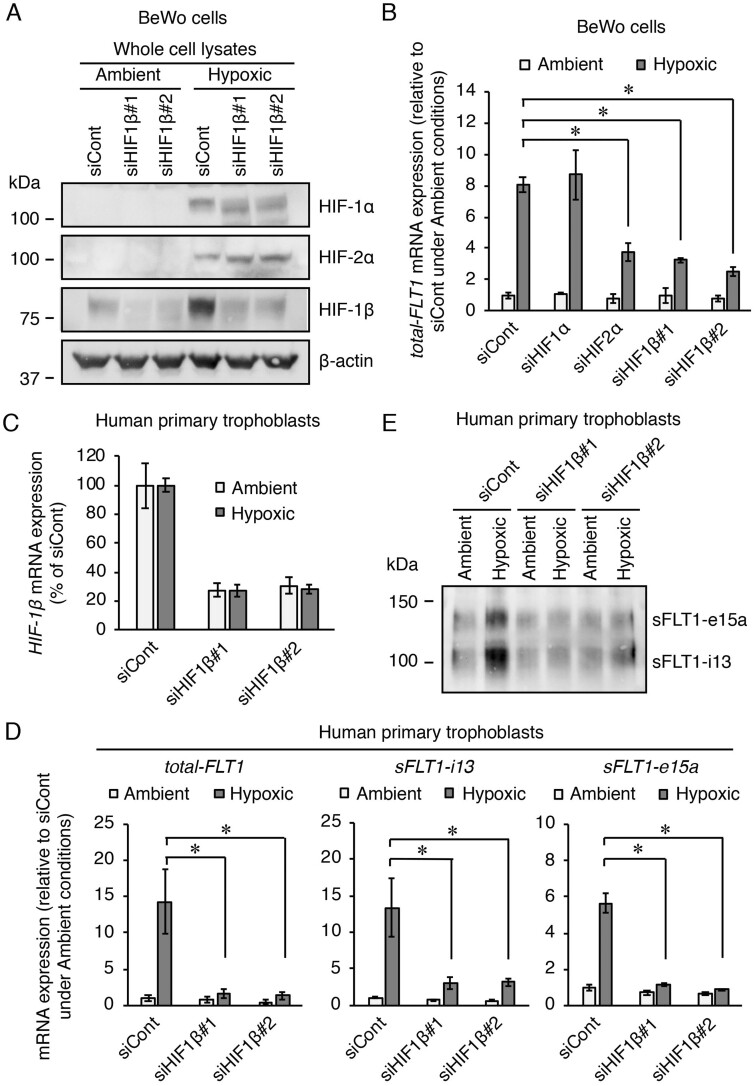
Figure 2.
Silencing of HIF-1β via transfection with a siRNA reduces the hypoxia-induced upregulation of the FLT1 gene in both BeWo cells and human primary trophoblasts. BeWo cells and primary trophoblasts were each transfected with a siRNA at 10 nM for 72 h and 48 h, respectively, after which the cells were incubated under ambient or hypoxic conditions for 24 h. (A) The protein expression levels of HIFs in the BeWo cells were assessed by western blotting analysis. (B) The mRNA expression levels of all FLT1 transcript variants (total-FLT1) in the BeWo cells were measured by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) using β-actin mRNA as a reference. Results are expressed as the fold change relative to the control siRNA (siCont)-transfected cells under ambient conditions. (C) Evaluation of the knockdown of the HIF-1β mRNA via transfection with siRNA in the primary trophoblasts. Results are expressed as a percentage relative to the control siCont-transfected cells under ambient or hypoxic conditions. (D) The mRNA expression levels of total-FLT1, sFLT1-i13 and sFLT1-e15a in the primary trophoblasts were measured by qRT-PCR using β-actin mRNA as a reference. Results are expressed as the fold change relative to the siCont-transfected cells under ambient conditions. (E) Western blotting of the sFLT1 proteins secreted by primary trophoblasts into the conditioned media. Uncropped images of the western blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. S4. All values are represented as the mean ± SD (n=3). Asterisks indicate the significant difference (P<0.05).