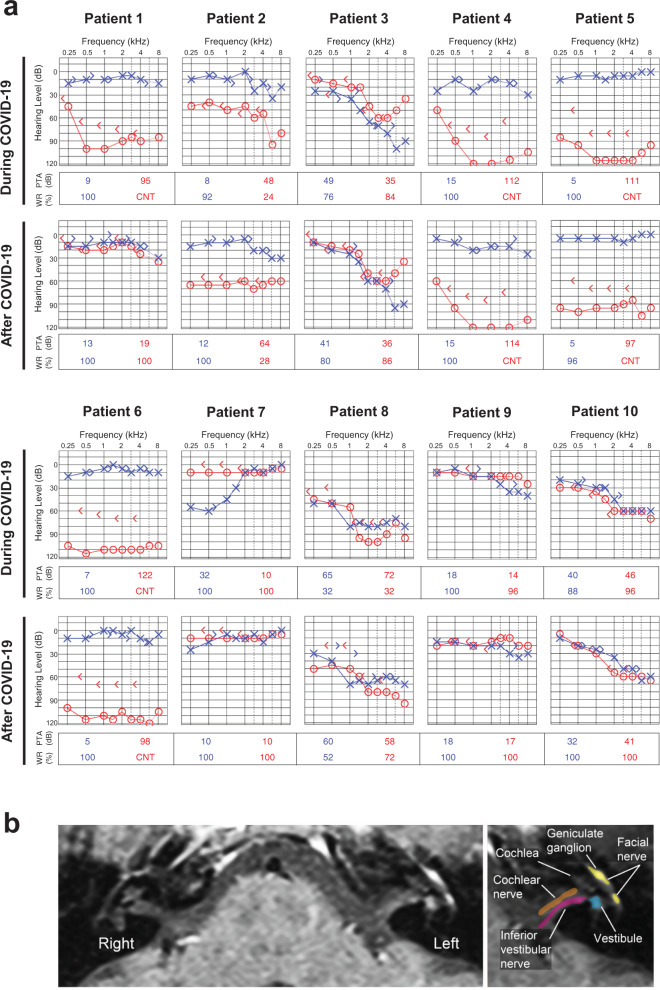
Fig. 1. Clinical data.
a Audiometry during (1st row) and after (2nd row) SARS-CoV-2 infection. Audiograms in the 2nd row were performed 4 months (patient 1), 2.5 months (patient 2), 4 months (patient 3), 3.5 months (patient 4), 2 months (patient 5), 2 months (patient 6), 4 months (patient 7), 4 months (patient 8), 2 months (patient 9), and 3 months (patient 10) after COVID-19. Audiometric thresholds are defined relative to normal hearing level defined by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI, 2010). A masking dilemma is seen in patients 1, 4, 5, and 6 with profound SNHL unilaterally and normal hearing contralaterally; the air-conduction thresholds are the actual hearing levels for these patients. Right ear (red) air conduction O, bone conduction <. Left ear (blue) air conduction X, bone conduction >. CNT = could not test/no response. PTA = the average of pure-tone audiometric thresholds at 0.5, 1, 2, and 3 kHz. WR = word recognition score, defined as the percentage of spoken monosyllabic words discernable from a list typically read at 70 dB or at the level at which a patient’s speech intelligibility curve plateaus. b Axial T1-weighted postcontrast MRI of the internal auditory canal of patient 7. Diffuse enhancement of the left geniculate ganglion, facial nerve, vestibule, cochlear, and vestibular nerves is seen. Facial nerve and geniculate ganglion (yellow), vestibule (blue), inferior vestibular nerve (purple), and cochlear nerve (orange) are colorized and superimposed over traditional images in the axial plane for the left ear.