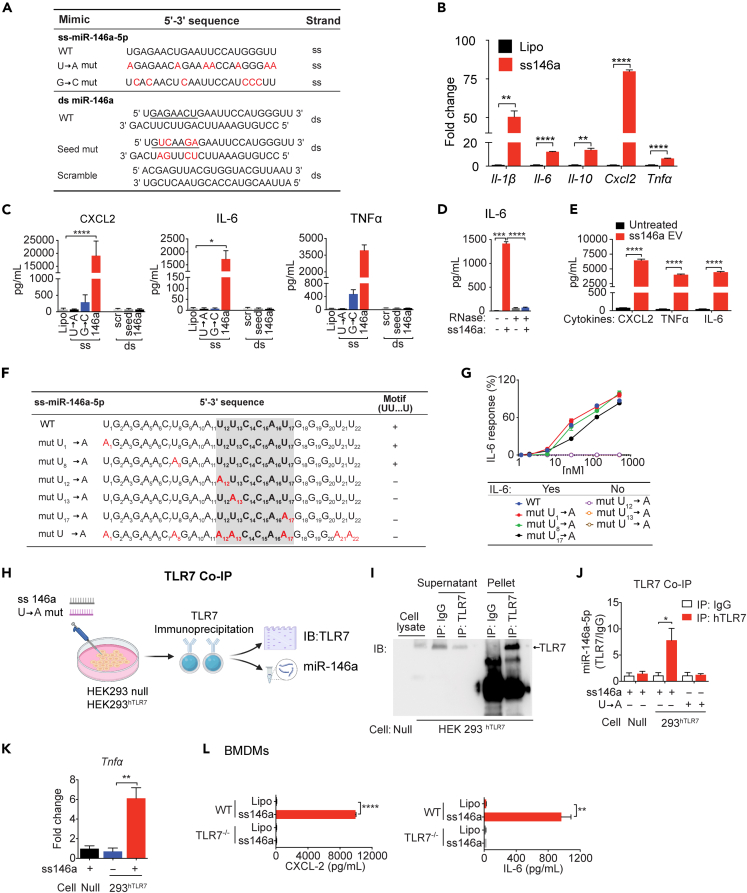
Figure 3.
Single-stranded (ss) miR-146a-5p induces proinflammatory cytokine production via its specific motif and TLR7 binding
(A) Nucleotide sequences of ss-miR-146a-5p, its duplex precursor (ds miR-146a), and their corresponding mutants. The seed region is underlined and mutations marked in red.
(B) ss-miR-146a-5p (50 nM) induces cytokine gene expression in BMDMs (n = 3).
(C) Production of cytokine proteins in BMDMs treated with miR-146a-5p (ss), miR-146a duplex (ds), their corresponding mutants at 50 nM, or lipofectamine only (Lipo) for 16 h.
(D) Effect of RNase A on ss-miR-146a-5p-induced IL-6 production. n = 3.
(E) EVs loaded with miR-146a-5p (0.3 pmol/16 μg EVs/100 μL) induces multiple cytokine productions in BMDMs.
(F) Nucleotide sequences of ss miR-146a-5p and its various U→A mutants. The U12U13…U17 motif sequence is highlighted in shade. U→A mutants are in red.
(G) Dose response of IL-6 production in BMDMs treated with miR-146a-5p or its various single U→A mutants (50 nM); n = 3.
(H) Schematic diagram of co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) experiments.
(I) Representative immunoprecipitation (IP) using IgG or anti-TLR7 Ab in HEK293-hTLR7 (293hTLR7) or null cells followed by immunoblot (IB) for TLR7.
(J) qRT-PCR analysis of ss-miR-146a-5p associated with hTLR7 IP (Null cell: n = 4, HEK293-hTLR7 cell: n = 6).
(K) ss-miR-146a-5p induces Tnfα gene expression in HEK293-hTLR7 cells but not in null cells. n = 3.
(L) WT, not TLR7−/−, BMDM’s response to ss-miR-146a-5p treatment with cytokine productions. n = 3.
∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, Welch t test.
Data are represented as mean ± SD.