Figure 1.
Amelioration of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)-like symptoms in Lyn–/– mice by heat shock protein gp96 immunization
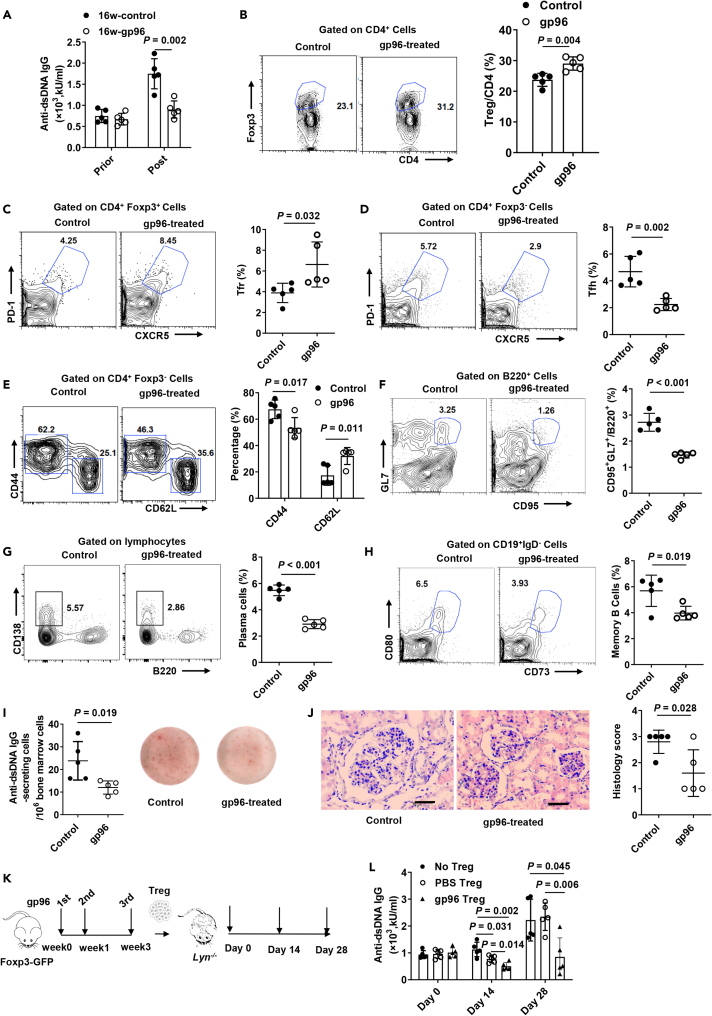
(A) Female Lyn–/– mice at 16 weeks old were immunized with 200 μg gp96 or saline as control (n = 5/group). Serum anti-dsDNA antibodies were determined using ELISA in Lyn–/– mice 1 week after the last immunization.
(B–E) FACS analysis of Foxp3+CD4+ Treg cells (B), CXCR5+PD-1+Foxp3+ Tfr cells, (C), CXCR5+PD1+Foxp3– Tfh cells (D) and activated conventional CD4+ T cells (CD44hi CD62Llow) (E) in the spleen of mice immunized at 16 weeks of age.
(F–H) FACS analysis of germinal center B cells (F), plasma cells (G) from the spleen, and memory B cells (H) from bone marrow.
(I) Absolute numbers of anti-dsDNA-specific antibody-secreting cells (ASCs) were determined using ELISPOT.
(J) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of kidney sections from 32-week-old Lyn–/– mice of indicated groups. Bar, 50 μm.
(K and L) Foxp3-GFP knock-in (KI) mice were immunized as in (K), and then Foxp3+ Treg cells were sorted and adoptively transferred into Lyn–/– mice. Serum was collected at the indicated times. Serum anti-dsDNA antibodies were determined using ELISA (L). The data are representative of two independent experiments with similar results. n = 5 mice/group. Mean ± SD is shown. The Student's t-test was used for statistical analysis. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.