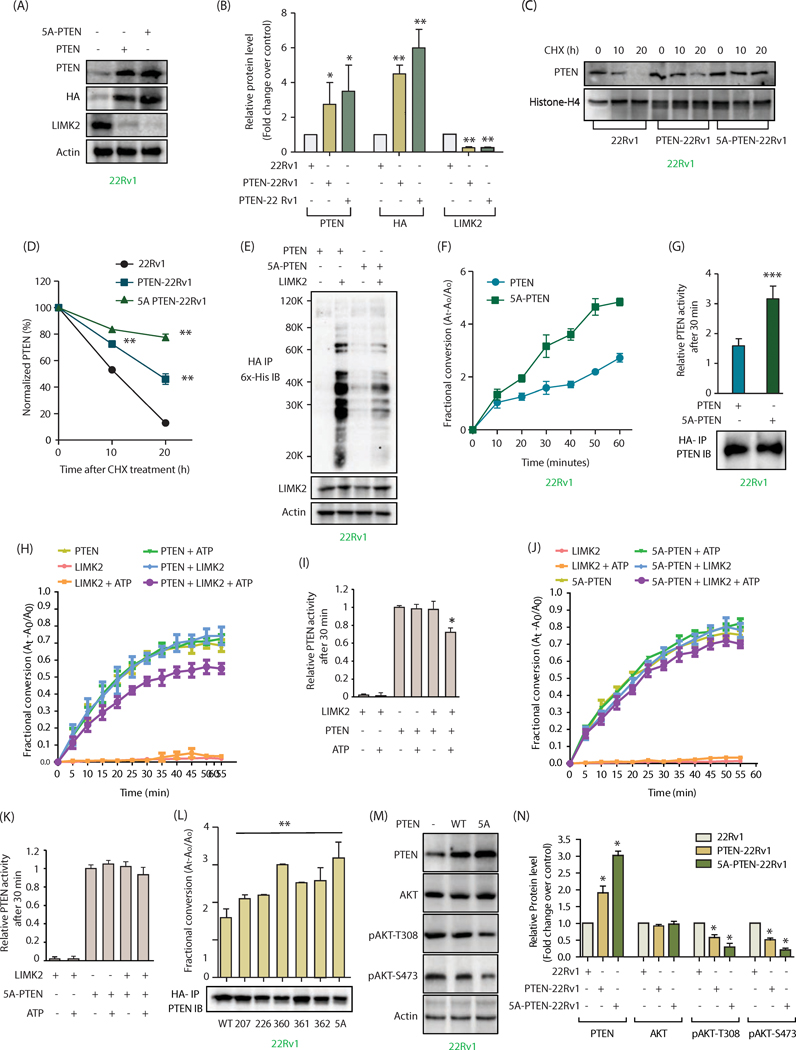
Figure 5:
LIMK2-mediated phosphorylation is responsible for increased ubiquitylation and inhibition of PTEN activity, causing AKT activation. (A) Phospho-resistant PTEN is expressed at higher levels compared to WT-PTEN in 22Rv1 cells. 22Rv1 cells were infected with HA-tagged wild-type PTEN or 5A-PTEN retrovirus for 36h, and protein levels of PTEN, LIMK2, HA and actin were analyzed using their respective antibodies. (B) The bar graph shows average values of wild type and mutant PTEN obtained from three independent experiments. Data shown are mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. *P <0.05, **P<0.005 compared to control cells. (C) LIMK2-mediated phosphorylation of PTEN decreases its stability. PTEN levels were analyzed in 22Rv1, PTEN-22Rv1 and 5A-PTEN-22Rv1 cells treated with cycloheximide for 10 and 20h. (D) Graphical representation of PTEN half-life in 22Rv1, PTEN-22Rv1 and 5A-PTEN-22Rv1 cells.**P<0.005. (E) LIMK2 overexpression significantly increased the ubiquitylation of WT-PTEN, as compared to 5A-PTEN in 22Rv1 cells. WT PTEN-22Rv1 and 5A-PTEN-22Rv1 cells were infected with 6x-His-Ubiquitin with or without LIMK2 retrovirus for 30h, followed by MG132 treatment for 12h. PTEN was immunoprecipitated using HA antibody and ubiquitylation analyzed using 6x-His antibody. (F) Phospho-resistant PTEN has increased phosphatase activity as compared to WT-PTEN. (G) Same data as Figure 5F showing PTEN phosphatase activity at 30 min in WT-PTEN-22Rv1 and 5A-PTEN-22Rv1 cells along with PTEN loading control. (H) LIMK2-mediated phosphorylation of PTEN decreases its phosphatase activity. PTEN was expressed and purified from SF9 insect cells and subjected to LIMK2 kinase assay. PTEN activity was calculated by measuring the absorbance of free phosphate over time at 620 nm using PIP3 as a substrate. (I) Same data as Figure 5H showing PTEN phosphatase activity at 30 min. (J) Phospho-resistant PTEN showed no significant change in phosphatase activity. (K) Same data as Figure 5J showing PTEN phosphatase activity at 30 min. Data obtained from three independent experiments was plotted as mean ± SEM of with *P <0.05 compared to control cells and **P<0.005 compared to control cells. (L) Effect of LIMK2-mediated phosphorylation on PTEN activity. Single mutants for each phosphorylation site were ectopically expressed in 22Rv1 cells and immunoprecipitated using HA antibody, phosphatase activity was assayed as before at 30 minutes and immunoblot for PTEN loading control is also shown. **P<0.005 compared to control cells. (M) Change in AKT phosphorylation in WT and 5A-PTEN cells. (N) Histogram shows change in AKT phosphorylation level in response to WT or 5A-PTEN expression. The data represented as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. *P <0.05 compared to control cells.