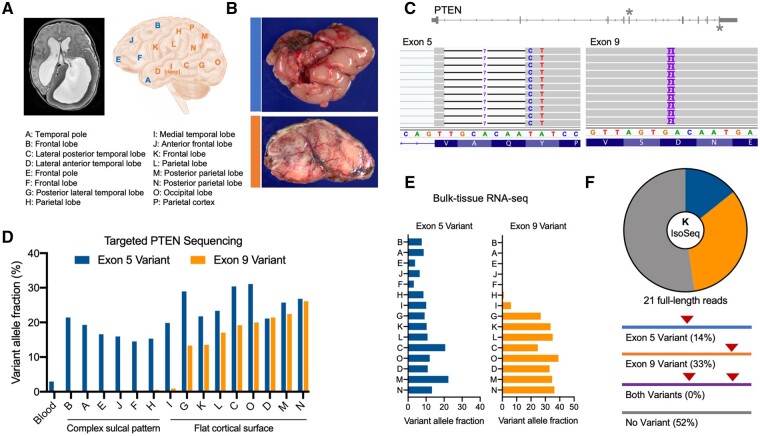
Figure 1.
Two somatic PTEN mutations identified in a patient with hemimegalencephaly patient. (A) MRI and sites of resected brain specimens obtained from a patient undergoing hemispherectomy for intractable epilepsy. See also Supplementary Fig. 1. (B) Gross pathology and SMI-32 immunohistochemistry show sites A and C exhibit either a complex sulcal pattern with abnormal cortical architecture (blue) or flattening and simplification of the cortical surface with enlarged neurons (orange). (C) Exome sequencing of site K reveals two distinct somatic mutations in exons 5 [chr10:89692771 (hg19); chr10:87933013 (hg38)] and 9 [chr10:89725125 (hg19); chr10:87965368 (hg38)] of PTEN. (D) Targeted DNA sequencing of all anatomical sites and blood showing the distribution and variant allele fractions of the two somatic mutations, which correlates with the observed neuropathology. (E) Variant allele fractions of each somatic variant in bulk RNA-seq data. See also Supplementary Fig. 2. (F) Long-read sequencing of PTEN transcripts from site K reveals that the two variants are on opposite alleles.