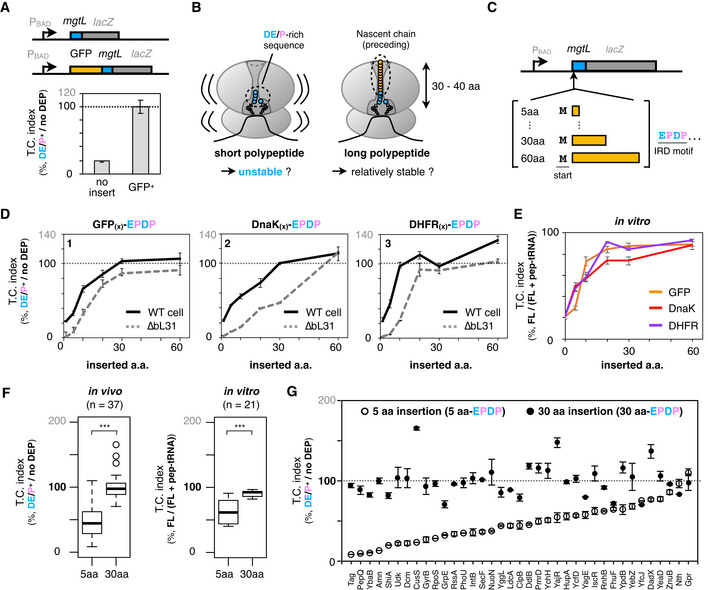
Figure 1. Exit tunnel‐occupying nascent polypeptides minimize the risk of IRD in their length‐dependent manners.
-
AIRD‐dependent translation attenuation by mgtL at the early (no insert, upper schematic) or middle (GFP+ , lower schematic) stage of translation elongation in vivo. Each of constructs with or without DE/P residues were expressed in E. coli, and β‐galactosidase activities were determined (Miller, 1972). The downstream translation frequency corresponding to IRD was calculated as the LacZ activity ratio [DE/P+ / no DEP], termed the translation continuation (TC) index. The mean values ± SE estimated from three independent biological and technical replicates are shown.
-
BSchematic of the working hypothesis that a tunnel‐occupying preceding nascent polypeptide stabilizes the translating ribosome to prevent IRD.
-
CSchematic of the mgtL‐lacZ variants, in which various lengths of the N‐terminal portions of GFP or other ORFs were inserted before the mgtL sequence.
-
DInserted amino acid length‐dependent IRD counteraction. The counteracting effects were expressed as the downstream translation continuities [DE/P+/no DEP] of each mgtL‐lacZ variant. The N‐terminal regions of E. coli GFP (panel 1), DnaK (panel 2), or DHFR (panel 3) were utilized as the preceding nascent polypeptides. Results of wild‐type (black line) and IRD‐prone ∆bL31 (dot line) cells are shown. The mean values ± SE estimated from three independent biological and technical replicates are shown.
-
EIRD‐counteracting effects of the N‐terminal insertions in a reconstituted in vitro translation system (PUREfrex). The ratio of the full‐length chain (FL) per aborted peptidyl‐tRNA (pep‐tRNA) accumulated in the PUREfrex reaction was calculated as the downstream translation continuation of each mgtL‐lacZ variant. The mean values ±SE estimated from three independent technical replicates are shown.
-
FIRD‐counteracting effect of short and long nascent polypeptides within the tunnel. Downstream translation continuation of mgtL‐lacZ variants with a 5 aa or 30 aa insertion (5 or 30 aa‐EPDP) in the in vivo reporter (left, n = 37) or the in vitro translation assay (right, n =21) are represented by boxplots using R software. Box portion and central band are described according to the 25th percentile and the median, respectively. ***P‐value < 0.001 (Welch’s t test).
-
GIndividual values of in vivo downstream translation continuation of the mgtL‐lacZ variants with the 5 aa‐ (white dots) or 30 aa‐EPDP constructs (black dots). N‐terminally inserted amino acid sequences are summarized in Appendix Table S4. The mean values ± SE estimated from three independent biological and technical replicates are shown.
