Figure EV4. (Related to Fig 4). Structure of Pol ε.
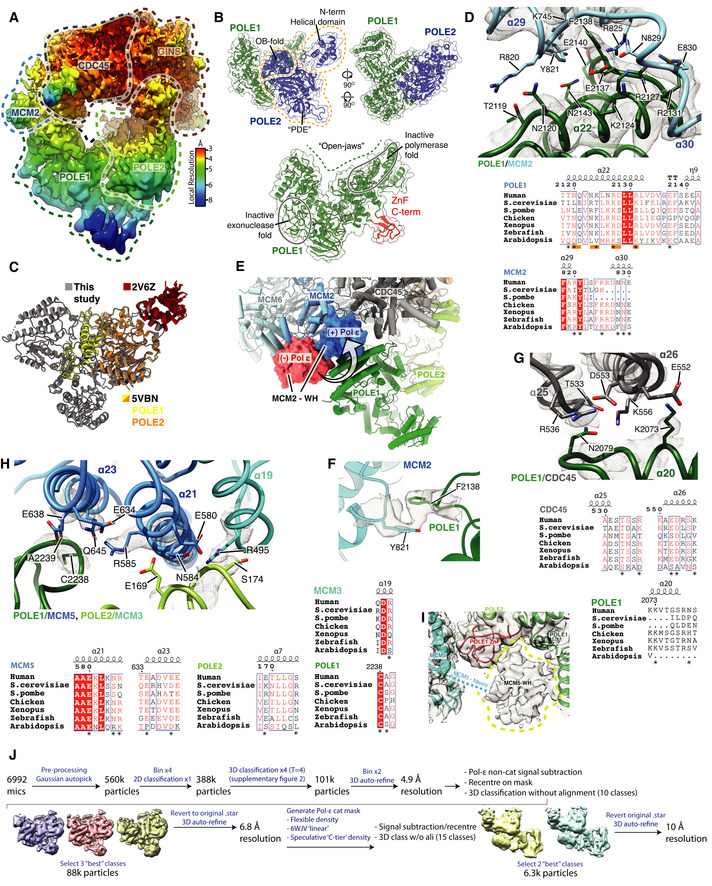
- Cryo‐EM map obtained using MultiBody refinement (Nakane et al, 2018) masking over the Pol ε non‐catalytic module, CDC45 and GINS. Map coloured by local resolution according to inset key.
- Model for the Pol εnon‐cat domain as part of the core human replisome (other replisome components not shown). Models displayed as cartoons overlayed with transparent surface rendering. (Top) POLE1 is coloured green and POLE2 in blue. POLE2 domains are annotated and their position indicated using dashed lines. (Bottom) Model for POLE1 displaying the “wide‐open jaw” configuration. Approximate positions of the inactive polymerase and exonuclease motifs are indicated and the C‐terminal ZnF coloured red.
- (Top) Detailed view of the interface between POLE1 (green) and the MCM2 winged‐helix domain (blue). Atomic models visualised using cartoon rendering with selected side chains displayed and corresponding cryo‐EM density is overlaid in transparent mesh. (Bottom) Multiple sequence alignment for residues involved in the MCM2‐WH/POLE1 interface. Orange bars indicate the pattern of charge conserved residues along the same face of POLE1 α22, residues that make inter‐protein contacts are marked with an asterisk. All alignments in the figure were carried out using NCBI Clustal Omega and visualised using ESPrit with the primary human sequence indicated. Uniprot ID for sequences used for POLE1 alignment: H. sapiens (Q07864‐1), S. cerevisiae (P21951‐1), S. pombe (P87154‐1), G. gallus (E1C5P2‐1), X. laevis (A0A1L8HZP3‐1), D. rerio (B0V351‐1), A. thaliana (F4HW04‐1). MCM2 alignment: H. sapiens (P49736‐1), S. cerevisiae (P29469‐1), S. pombe (P40377‐1), G. gallus (F1NB20‐1), X. laevis (P55861‐1), D. rerio (A0A0R4IF65‐1), A. thaliana (Q9LPD9‐1).
- Model highlighting the repositioning of the MCM2 WH domain following Pol ε engagement with CMG. Replisome model displayed using cylinder and stub cartoon rendering. The position of the MCM2 WH domain is displayed using surface rendering in the absence of Pol ε (Rzechorzek et al, 2020) (red) and presence (blue).
- Model visualising the ring‐stacking interaction between MCM2 Y821 (blue) and POLE1 F2138 (green). Cryo‐EM density is displayed as a transparent surface.
- (Top) Detailed view of the interface between POLE1 and the CDC45 as shown as in (C). (Bottom) Multiple sequence alignment for residues involved in the POLE1/CDC45 interface. Residues that make inter‐protein contacts are marked with an asterisk. Uniprot ID for sequences used for POLE1 alignment is as described in (C) and Uniprot IDs used for the CDC45 alignment are as described in Fig EV2D.
- (Top) Detailed view of the interface involving POLE1, POLE2 and MCM5 as shown as in (C). (Bottom) Multiple sequence alignment for residues involved in the POLE1/POLE2/MCM5 interface. Residues that make inter‐protein contacts are marked with an asterisk. Uniprot ID for sequences used for POLE1 alignment are as described in panel b. Uniprot IDs used for POLE2 alignment: H. sapiens (P56282‐1), S. cerevisiae (P24482‐1), S. pombe (O94263‐1), G. gallus (Q5ZKQ6‐1), X. laevis (Q9DGB4‐1), D. rerio (Q8JHG8‐1), A. thaliana (Q500V9‐1). MCM5 alignment: H. sapiens (P33992‐1), S. cerevisiae (P29496‐1), S. pombe (P41389‐1), G. gallus (Q5ZKL0‐1), X. laevis (P55862‐1), D. rerio (F1QK71‐1), A. thaliana (O80786‐1).
- Low threshold cryo‐EM map, displayed as a transparent grey surface, for the complete core human replisome highlighting unmodelled density, in the same location as the MCM5 winged‐helix domain in previous S. cerevisiae structures, circled with a dashed yellow line.
- Schematic describing the processing pipeline used to obtain a cryo‐EM reconstruction containing additional ordered density for the Pol ε catalytic module.
