Figure EV5. (Related to Fig 6). Identification of CLASPIN docking sites on the human replisome.
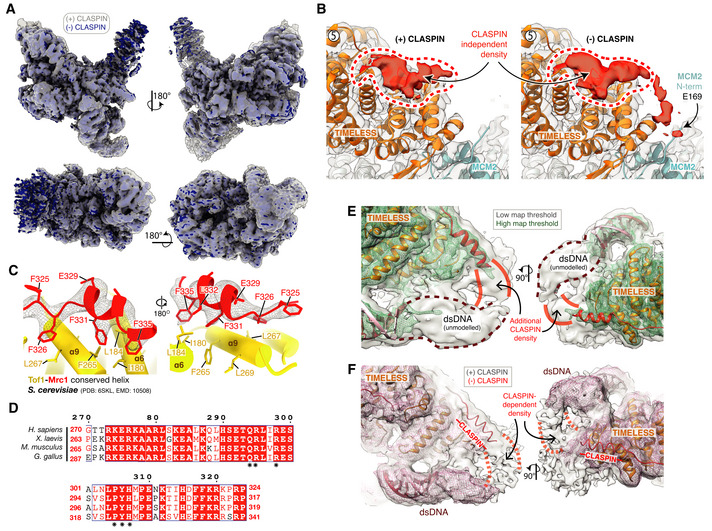
- Cryo‐EM reconstruction of the core human replisome in the presence of CLASPIN (grey) rigid‐body‐docked into the cryo‐EM reconstruction in the absence of CLASPIN (blue) using UCSF Chimera (Pettersen et al, 2004) (correlation 0.8993).
- Detailed view of the CLASPIN independent density that is bound to the N‐terminal end of the TIMELESS α‐solenoid. (Left) density in the presence and (right) absence of CLASPIN.
- Closeup view of the interface between Mrc1 residues F335‐F325 and Tof1. The Mrc1 model was built into unmodelled density present in the S. cerevisiae replisome (PDB: 6SKL, EMD: 10508). Tof1 α6 and α9 are structurally equivalent to TIMELESS helices α8 and α11, respectively. Tof1 and Mrc1 are visualised using cartoon rendering with density assigned to Mrc1 displayed as grey mesh.
- Multiple sequence alignment for H. sapiens CLASPIN residues 270–324 at CLASPIN site 1. CLASPIN residues involved in contacting the replisome are marked with an asterisk. Alignments carried out using NCBI Clustal Omega (Sievers & Higgins, 2014) and visualised using ESPrit (Robert & Gouet, 2014) with the primary sequence indicated. Uniprot ID for sequences used for CLASPIN alignment: H. sapiens (Q9HAW4‐1), M. musculus (Q80YR7‐1), G. gallus (F1P0J7‐1), X. laevis (Q9DF50‐1).
- Cryo‐EM map for the core human replisome in the presence of CLASPIN at both high (green mesh) and low (grey transparent surface) thresholds, indicating the presence of density, continuous with CLASPIN site #1, projecting towards the upstream parental DNA duplex.
- Cryo‐EM map of the core human replisome in the presence of CLASPIN (grey transparent surface) and absence (red mesh) both at low thresholds. Indicates that density projecting from CLASPIN‐dependent site #1 towards the unmodelled parental DNA duplex is dependent upon CLASPIN.
