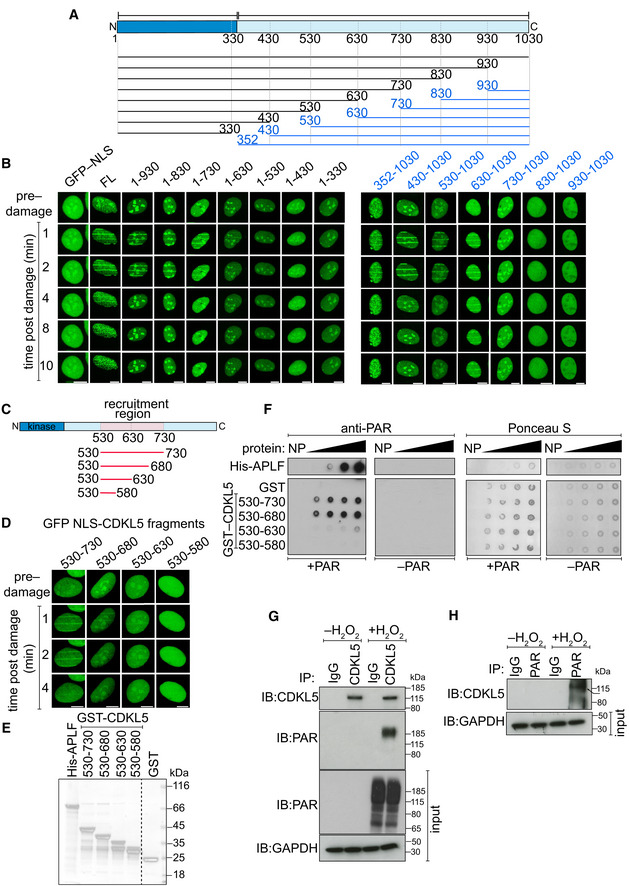
Figure 2. CDKL5 recruitment domain binds PAR directly.
-
ASchematic diagram of CDKL5 deletion mutants, deleting from the N‐terminal (blue) or C‐terminal (black) ends. All proteins were expressed with an N‐terminal NLS and GFP tag.
-
BBrdU‐sensitized U‐2‐OS (Flp‐In T‐REx) cells stably expressing GFP‐NLS, the GFP‐NLS‐CDKL5 deletion mutants shown in (A) or full length (FL) GFP‐NLS‐CDKL5 was subjected to line micro‐irradiation (355 nm) and time‐lapse imaging. Three independent experiments were performed, and one representative experiment is shown. Scale bar is 10 μm.
-
CSchematic for fragments corresponding to the PAR‐dependent recruitment region in CDKL5 as identified in (B).
-
DSame as in (B) except that the GFP‐NLS‐tagged CDKL5 fragments indicated were examined. Scale bar is 10 μm.
-
ECoomassie gel showing recombinant fragments of human CDKL5 fused to GST purified from bacterial lysates. GST and APLF were also purified as controls.
-
FRecombinant fragments of CDKL5 fused to GST (1.2, 2.5, 5, 10 µg), or GST, were dot‐blotted on nitrocellulose membrane and then incubated with synthetic PAR. PAR binding was detected by far Western blotting. APLF was used as positive control. One of three independent experiments is shown.
-
G, HU‐2‐OS (Flp‐In T‐Rex) cells stably expressing CDKL5 were either mock‐treated or treated with 500 µM H2O2 for 30 min. Extracts were subjected to immunoprecipitation with antibodies against CDKL5 (G) or PAR (H) (or non‐specific IgG as control). Precipitates, and input lysates, were analysed by Western blotting using the indicated antibodies. One of two independent experiments is shown.
Source data are available online for this figure.
