Figure EV2. Restricting CDKL5 expression to the cell nucleus.
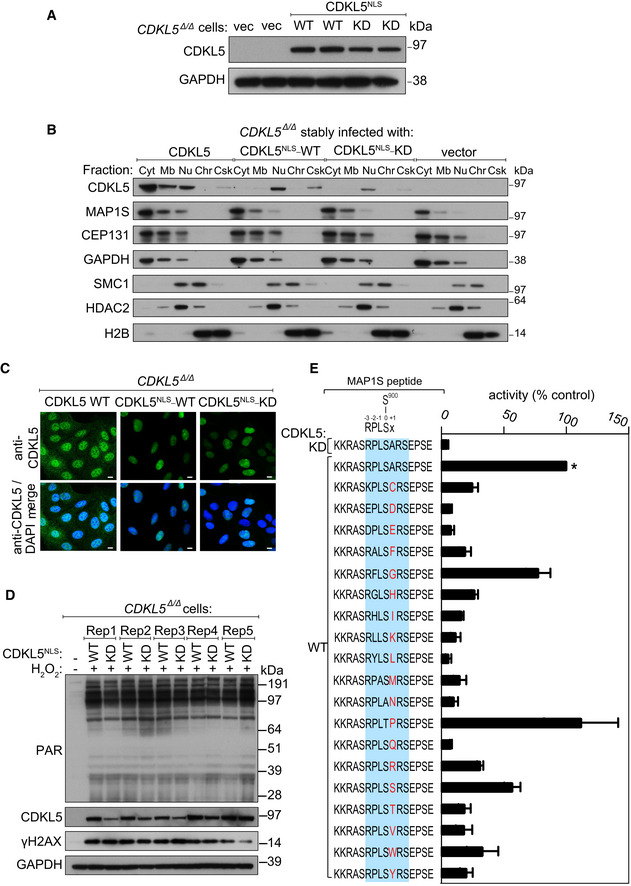
- Extracts of CDKL5‐disrupted U‐2‐OS (Flp‐In T‐REx) cells (CDKL5 Δ/Δ) stably expressing CDKL5NLS WT or a K42R kinase‐dead mutant (CDKL5NLS–KD) or empty vector were subjected to Western blotting with the antibodies indicated. Two different dishes of cells are shown per condition.
- Subcellular fractionation of lysates from CDKL5 Δ/Δ cells stably expressing CDKL5, CDKL5NLS WT or CDKL5NLS KD or empty vector. Lysates were fractionated to isolate proteins found in the following subcellular compartments: cytoplasmic (Cyt), membrane (Mb), nuclear (Nuc), chromatin (Ch) or cytoskeleton (Csk). Fractionated samples were resolved by SDS–PAGE and probed with antibodies shown.
- CDKL5 Δ/Δ cells stably expressing CDKL5, CDKL5NLS WT or CDKL5NLS KD were subjected to indirect immunofluorescence analysis with anti‐CDKL5 antibodies. Scale bar is 10 μm.
- CDKL5 Δ/Δ cells stably expressing CDKL5NLS WT or CDKL5NLS KD (or empty vector) were treated with 500 µM H2O2 for 15 min. Samples were resolved by SDS–PAGE and probed with indicated antibodies or stained with Ponceau S to show equal loading. Rep=biological replicate.
- Peptide kinase assays to investigate CDKL5 sequence specificity. Anti‐FLAG precipitates from HEK293 cells transiently expressing FLAG‐tagged CDKL5 (wild‐type “WT” or a K42R kinase‐dead “KD” mutant) were incubated with synthetic peptides corresponding to sequence around the previously reported CDKL5 phosphorylation site in MAP1S (Ser900) designed specifically to investigate the effect of amino acid substitutions A901 on the phosphorylation of MAP1S Ser900. Assays were done in the presence of [γ‐32P]‐labelled ATP‐Mg2+, and peptide phosphorylation was measured by Cerenkov counting. Phosphorylation of the control wild‐type MAP1S peptide is taken as 100% (*). The data are represented as mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. The RPXSA motif is shaded in blue, and amino acid substitutions compared with the wild‐type MAP1S Ser900 peptide are shown in red.
Source data are available online for this figure.
