Figure 8. Kinase activity of CDKL5 facilitates transcriptional silencing.
-
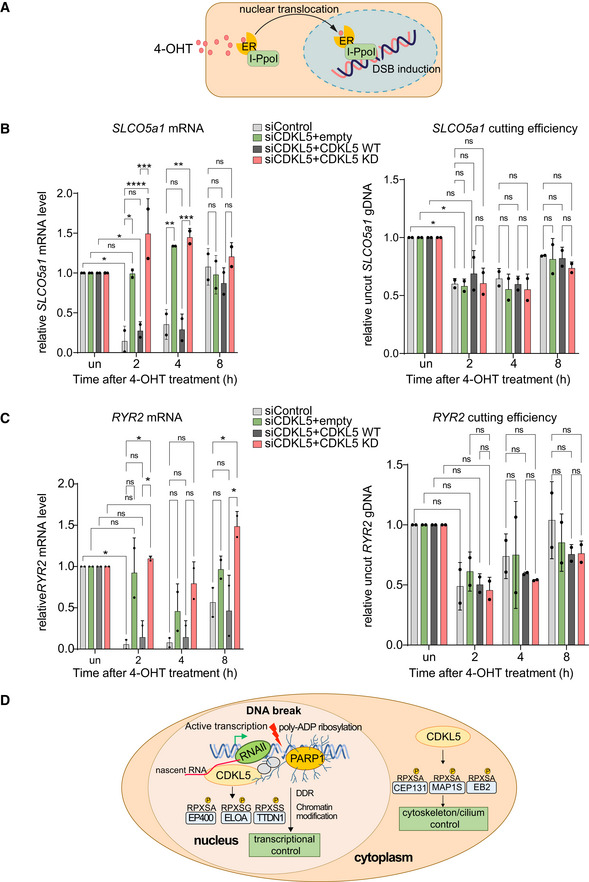
ASchematic diagram of the I‐PpoI system for inducing DNA breaks in the nuclear human genome. Addition of 4‐OHT to U‐2‐OS‐pEP15 cells stably expressing the I‐PpoI endonuclease fused to the estrogen receptor (ER) induces nuclear translocation of the fusion protein and cleavage cleavage of FokI recognition sites in nuclear DNA resulting, leading to DSB induction.
-
B, CQuantitative PCR with reverse transcription (qRT–PCR) analysis of SLCO5a1 (B) and RYR2 expression levels (C) (left panels) U‐2‐OS HA‐ER‐I‐PpoI cells depleted of CDKL5 transiently transfected with FLAG‐tagged CDKL5 wild‐type (WT) or a K42R‐mutated kinase‐dead (KD) mutant, or empty vector, at the times indicated after inducing I‐PpoI. The mean ± SD from two qPCR replicates of two independent experiments is shown. Statistical significance for all the data was assessed by two‐way ANOVA test *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 and ****P < 0.0001; ns—not significant. I‐PpoI‐mediated cutting efficiency in the relevant gene is shown in the right‐hand panel (see Materials and Methods).
-
DSchematic diagram depicting CDKL5 functions in nucleus and cytosol.
Source data are available online for this figure.
