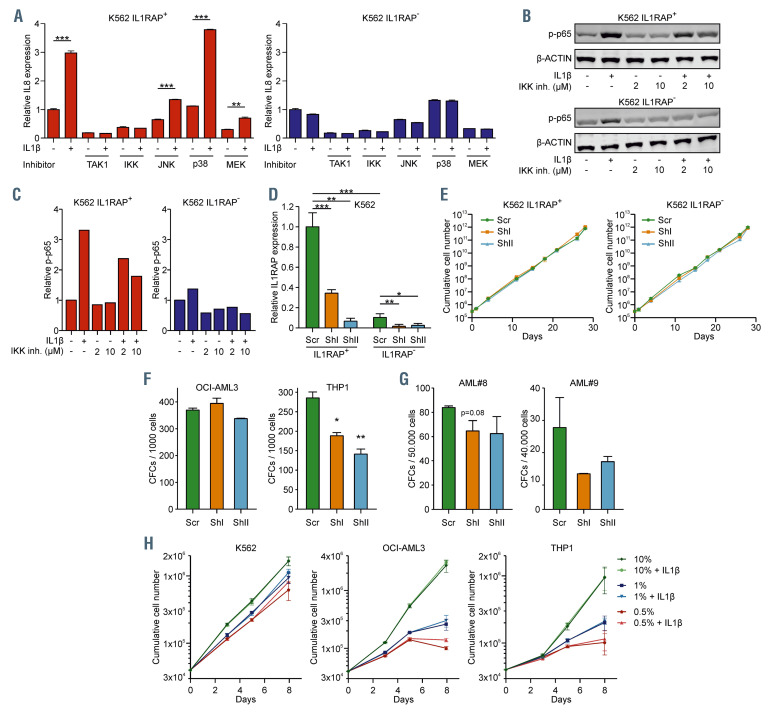
Figure 3.
IL1-IL1RAP mediated activation of the NFkB signaling does not rescue proliferation under stress conditions, but IL1RAP knockdown results in reduced colony-forming capacity. (A) Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) analysis in K562 IL1RAP+ and IL1RAP– cells treated with TAK1, NFkB, JNK, p38 and MEK inhibitors and subsequently stimulated with IL1b. Bars indicate mean ± standard deviation (SD) of technical triplicates. (B) Western blot of K562 IL1RAP+ and IL1RAP- treated with or without IL1b and/or IKK inhibitor (IKK inh). (C) Quantification of western blot in panel C, p-p65 was normalized to b-ACTIN. (D) Interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein (IL1RAP) mRNA levels measured by qPCR in K562 IL1RAP+ and IL1RAP- cells transduced with short hairpin (shRNA) including a non-targeting control (scr) and shRNA targeting IL1RAP (shI and shII). Bars indicate mean ± SD of technical triplicates. (E) Growth curves of K562 IL1RAP+ and IL1RAP- cells (n=3) ± knockdown of IL1RAP. (F) Colony-forming cell (CFC) output of OCI-AML3 and THP1 ± knockdown of IL1RAP. Bars indicate mean ± SD of technical duplicates. (G) CFC output of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patient 8 (AML#8) and AML#9 ± knockdown of IL1RAP. Bars indicate mean ± SD of technical duplicates. (H) Growth curves after serum depletion of K562, OCI-AML3 and THP1 cells (n=3) ± IL1b. Statistical analysis in all panels was performed using a Student’s t-test. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001.