Figure 4.
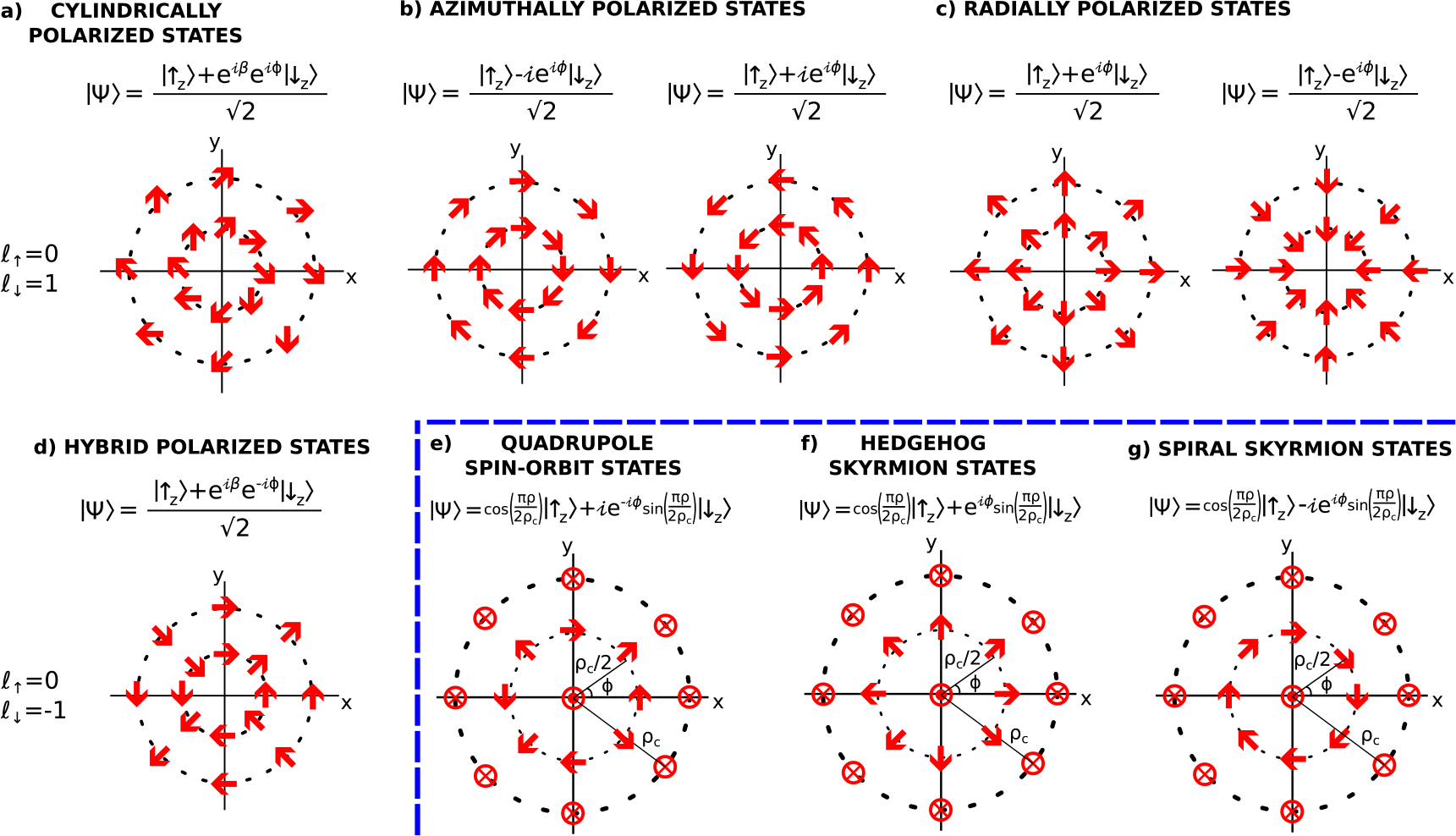
The spin orientation (red arrows) of the spin-orbit states with a coupling between ℓ↑ = 0 and ℓ↓ = ± 1, where the axis points out of the page. In analogy to optical OAM terminology, we may classify four categories of spin-orbit states with radially independent spin orientations: (a) ‘cylindrically polarized states’ where the spin orientation is given by , where β is an arbitrary phase; (b) ‘azimuthally polarized states’ which are a subset of cylindrically polarized states where ; (c) ‘radially polarized states’ which are a subset of cylindrically polarized states where ; and (d) ‘hybrid polarization states’ where , where β is an arbitrary phase. Note that all of the states with a certain {ℓ↑, ℓ↓} differ by a phase on the spin DOF. The preparation techniques shown in figure 1 can also produce spin-orbit states with radially dependent spin orientations. The main three categories are: (e) quadrupole spin-orbit states as described by equation (12); (f) hedgehog skyrmion states; and (g) spiral skyrmion states. An array of any of these three states can be obtained via the appropriate LOV prism pair combination.
