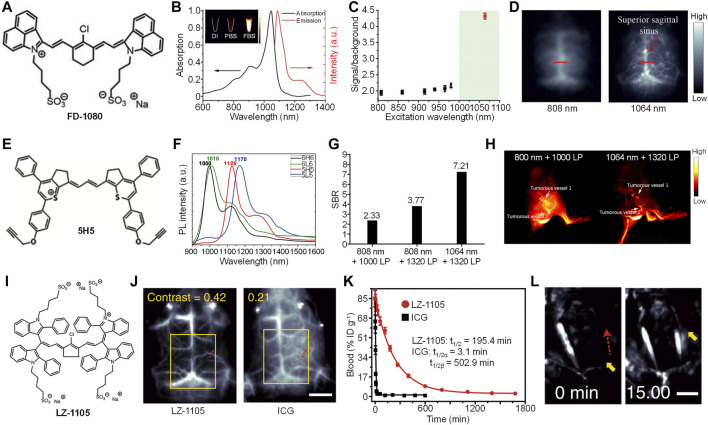
FIGURE 1.
(A) Chemical structure of cyanine-based dye (FD-1080). (B) Absorption and emission spectra of FD-1080. Inset: Representative second near-infrared window (NIR-II) fluorescence images of FD-1080 in deionized (DI) water, PBS, and fetal bovine serum (FBS) under 1,064 nm excitation. (C) The signal-to-background ratio of mouse left hindlimb vasculature injected with FD-1080-FBS under different excitation wavelengths. (D) Representative NIR-II fluorescence images of mouse brain vasculature injected with FD-1080-FBS under 808 or 1,064-nm excitation. (E) Chemical structure of 5H5. (F) Fluorescence spectra of 6H6, 6L6, 5H5, and 5L5. (G) The signal-to-background ratio of mouse hindlimb vasculature injected with 5H5 under different excitation wavelengths and filters. (H) Representative NIR-II fluorescence images of mouse blood vessels around and within tumor under different excitation wavelengths and filters. (I) Chemical structure of LZ-1105 (J) Representative NIR-II fluorescence images of mouse brain injected with LZ-1105 or indocyanine green (ICG) under 1,064 and 808 nm excitation, respectively. The scale bar represents 3 mm (K) Blood concentration of LZ-1105 and ICG in living mice as a function of time (L) Representative NIR-II fluorescence images of LZ-1105-injected mouse carotid artery before and after injection of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for 15 min. The scale bar represents 3 mm. Adapted from ref. 19–21. Copyright© 2018 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH and Co. KGaA, Weinheim, 2019 American Chemical Society and 2020 Springer Nature.