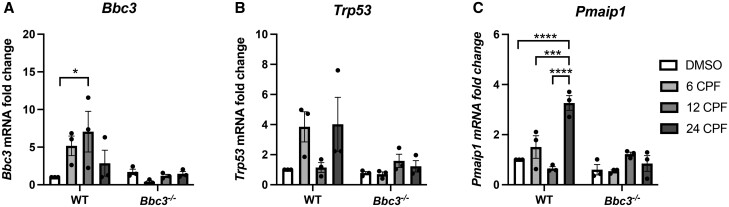
Figure 2.
Intrinsic apoptosis-related transcripts are up-regulated in a Bbc3-dependent manner upon chlorpyrifos (CPF) exposure. Primary cortical neuronal cultures were established from WT and Bbc3−/− embryos (E14.5–E16.5) and treated with vehicle (DMSO) or 50 µM for 6, 12, or 24 h. RNA was collected using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen). Equal quantities of mRNA normalized across samples were reversed transcribed into cDNA using the iScript cDNA Synthesis Kit. (A) Bbc3, (B) Trp53 (encodes for the protein p53), and (C) Pmaip1 (encodes for the protein NOXA) transcripts were analyzed and relative levels determined using the CFX96 Touch Real-Time PCR Detection System. CPF treatment induced Bbc3 expression, with significant elevation observed at 12 h (2-way ANOVA, **p = .0051 [genotype], nsp = .1902 [treatment], and nsp = .0610 [genotype × treatment]; WT 24 DMSO to WT 12 CPF *p = .0190). Variable Trp53 expression with CPF treatment was observed (2-way ANOVA, *p = .0176 [genotype], nsp = .1281 [treatment], nsp = .0758 [genotype × treatment]). Treatment with CPF elevated Pmaip1 expression in a genotype-specific manner (2-way ANOVA, ***p = .0002 [genotype], ***p = .0002 [treatment], ****p < .0001 [genotype × treatment]) with the greatest induction observed at the 6 and 24 h timepoints (WT 24 DMSO to WT 24 CPF, ****p < .0001; WT 6 CPF to WT 24 CPF, ***p = .0004; WT 12 CPF to WT 24 CPF, ****p < .0001). Data are representative of 3 biologic replicates.