Figure 5:
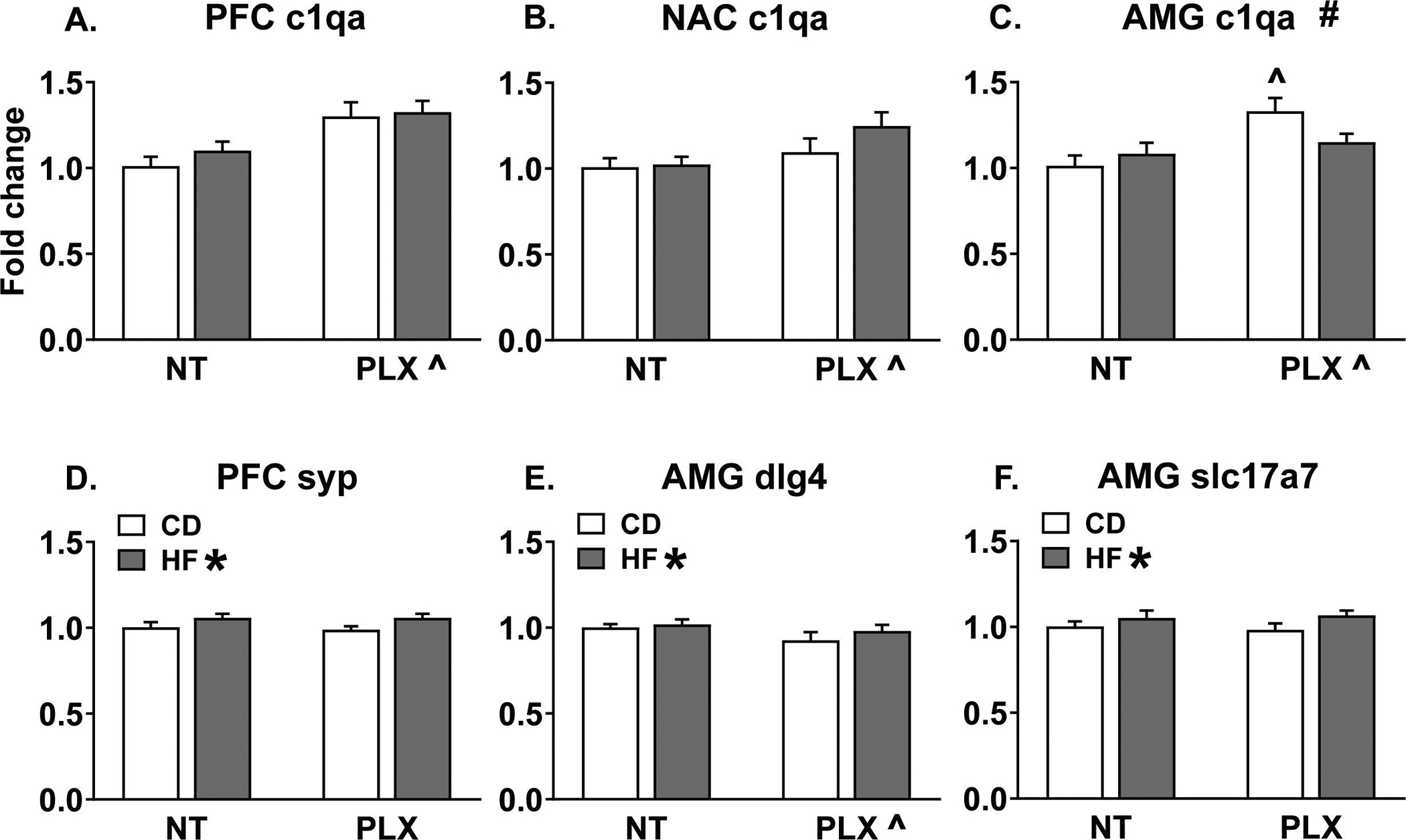
Adolescent PLX treatment increased c1qa expression measured in adult males in the (A) PFC, (B) NAC, and (C) AMG. In the AMG, this effect was specific to the CD group. (D) Maternal HF diet increased synaptophysin expression in the PFC. (E) Maternal HF diet increased AMG dlg4 (psd95) expression while PLX treatment reduced it. (F) Maternal HF diet increased slc17a7 (vglut1) expression in the AMG. (n = 7–8/group) (HF = offspring of maternal high fat diet; CD = offspring of maternal control diet; PLX = adolescent PLX3397 treatment; NT = not treated during adolescence) (Graph title # = significant interaction between perinatal diet and adolescent treatment; HF * = main effect of perinatal high fat diet; PLX ^ = main effect of adolescent treatment; ^p < 0.05 vs. CD NT)
