Figure 6:
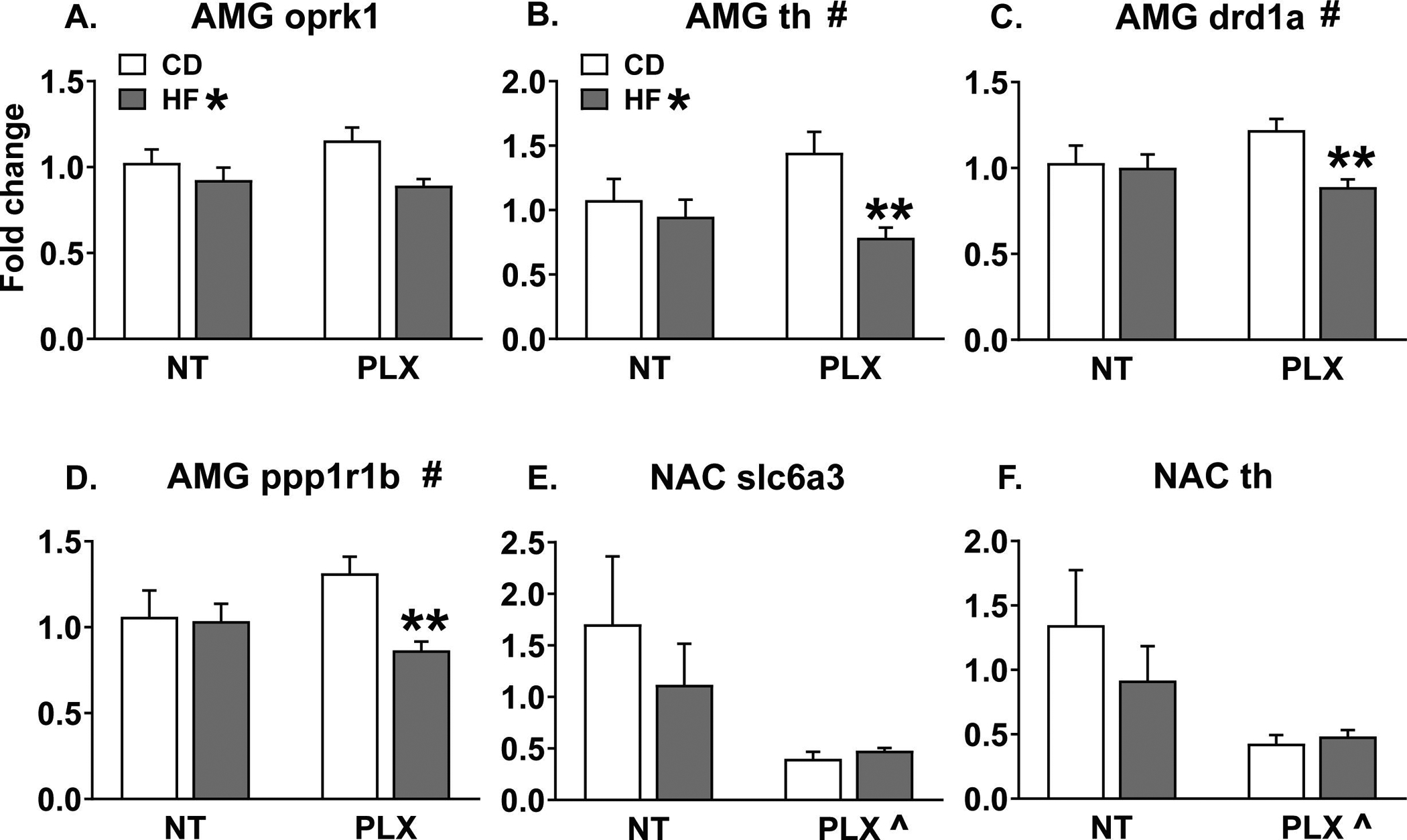
In the adult male AMG, maternal HF diet decreased (A) oprk1 and (B) TH expression and interacted with adolescent PLX treatment to reduce (B) TH, (C) drd1a, and (D) ppp1r1b (darpp32) expression specifically in the PLX group. In the NAC, PLX treatment decreased (E) slc6a3 (DAT) and (F) TH expression. (n = 7–8/group) (HF = offspring of maternal high fat diet; CD = offspring of maternal control diet; PLX = adolescent PLX3397 treatment; NT = not treated during adolescence) (Graph title # = significant interaction between perinatal diet and adolescent treatment; HF * = main effect of perinatal high fat diet; PLX ^ = main effect of adolescent treatment; **p < 0.05 vs. CD PLX)
