Figure 6 .
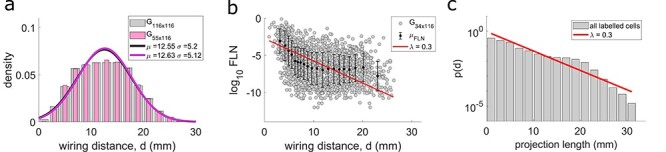
Exponential distance rule. (a) Distribution of the interareal wiring distances among all 116 areas (gray bars) and between the target-source pairs of areas (pink bars). Bin size is 2 mm. Solid lines are Gaussian fits to the data. The normal distributions for these 2 samples of data indistinguishable (2-sided 2-sample Kolmogorov–Smirnov test: 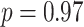 ). (b) The base 10 logarithm of the fraction of the extrinsic labeled neurons
). (b) The base 10 logarithm of the fraction of the extrinsic labeled neurons 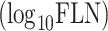 as a function of interareal wiring distance. Black dots and error bars are the mean and standard deviation within a window of 173 data points (bin size is 20) and the red plot is the same as in (c). (c) The histogram of the projection lengths of all labeled neurons (both intrinsic (551 664 labeled neurons) and extrinsic (1 414 364 labeled neurons), in total 1 966 028 labeled neurons). Bin size is 2 mm and the bars are the counts of the projection lengths lying in the bin size divided by the total number of the projections. The red line is a linear fit to the base 10 logarithm values of the histogram
as a function of interareal wiring distance. Black dots and error bars are the mean and standard deviation within a window of 173 data points (bin size is 20) and the red plot is the same as in (c). (c) The histogram of the projection lengths of all labeled neurons (both intrinsic (551 664 labeled neurons) and extrinsic (1 414 364 labeled neurons), in total 1 966 028 labeled neurons). Bin size is 2 mm and the bars are the counts of the projection lengths lying in the bin size divided by the total number of the projections. The red line is a linear fit to the base 10 logarithm values of the histogram 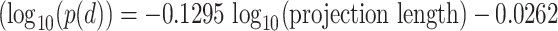 giving
giving 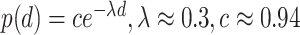 , where d is the projection length).
, where d is the projection length).
