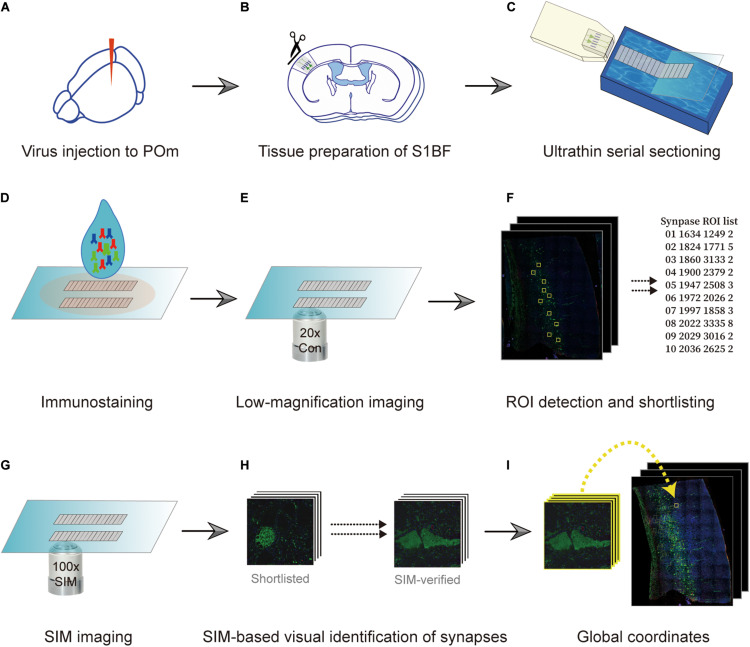
FIGURE 1.
Overview of the imaging technique. (A) Fluorescence labeling of synapses-of-interest. Neurons in the posteromedial nucleus of the thalamus (POm) were labeled using stereotactically delivered adeno-associated virus (serotype 1) transduction of tdTomato in a Thy1-EGFP (type M) mouse. After 4 weeks, the mouse was sacrificed and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde. (B) Embedding. Subsequently, the S1BF region was embedded in Lowicryl resin. (C,D) Serial sectioning and immunostaining. A series of 90 nm sections were collected (C) and immunostained with antibodies against synaptophysin-1, GFP, and tdTomato (D). (E,F) Low-magnification imaging and ROI detection. The series of sections were imaged at 20x resolution, and the global coordinates of ROIs were computed based on the existence of overlapping color channels. (G) SIM imaging. ROIs were revisited, and SIM images of the regions were acquired. (H,I) Determination of synapse locations. SIM images were post-processed to render the synapse images and visually determine if the structure indeed formed synapses (H). True synapses were relocated on the low-magnification image with image registration (I).