Figure 5. The pro-inflammatory effect of WD is abrogated by antibiotic treatment.
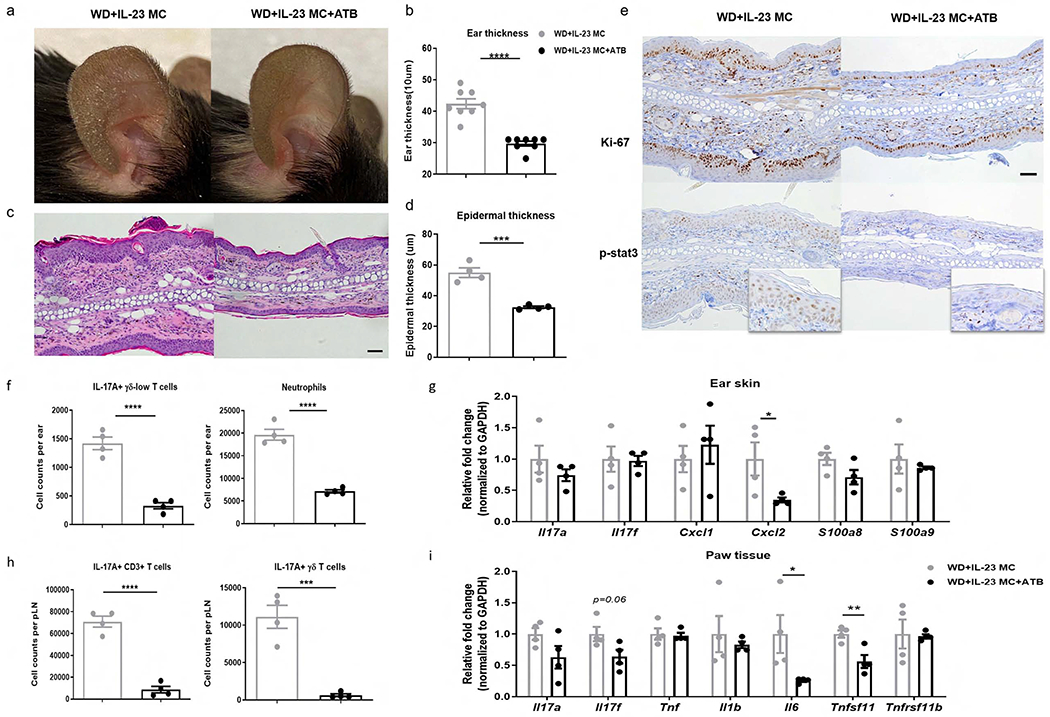
WD-fed C57BL/6 mice were treated with broad-spectrum combination antibiotics (ATB) or vehicle daily for 6 weeks by oral gavage and then injected with IL-23 MC to initiate disease. (a) Representative photographs, (b) ear thickness, (c) image of H&E section (scale bars, 50 μm), (d) histological analysis of epidermal thickness, (e) representative images of immunohistochemical Ki-67 and p-stat3 (scale bars, 50 μm), (f) absolute numbers of IL-17A-producing γδ-low T cells and neutrophils, and (g) gene expression of proinflammatory markers in ear skin. (h) Absolute numbers of IL-17A-producing CD3+ T cells and γδ T cells in popliteal LN. (i) Gene expression of proinflammatory cytokines and osteoclastogenesis-related markers in paw tissue. All of the data are presented as mean± SEM. 4 mice per group. Data are representative of two independent experiments. * p <0.05, ** p <0.01. *** p <0.001, by using Student’s t-test.
