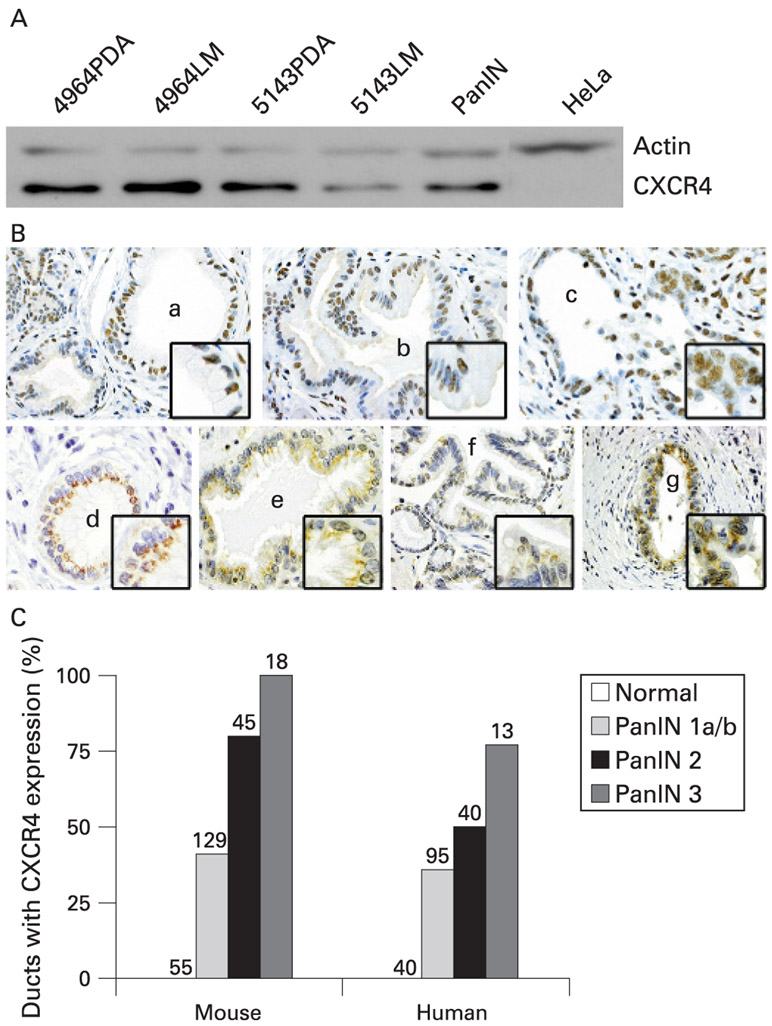
Figure 1.
The chemokine receptor CXCR4 is expressed in murine and human pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia. (A) Immunoblotting of cell lysates derived from PdxCre/LSL-KrasG12D mice included two primary pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma lines (4964PDA, 5143PDA), two metastatic lines (4964LM, 5143LM), and a pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN) cell line which all demonstrate strong expression of CXCR4. (B) Mouse (mPanIN) and human (hPanIN) pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia demonstrate increased expression of CXCR4 with progression from PanIN 1A to PanIN 3 with an absence of expression in normal duct. Representative samples are shown and include (a) mPanIN 1A, (b) mPanIN 1B, (c) mPanIN 3, (d) hPanIN 1A, (e) hPanIN 1B, (f) hPanIN 2, and (g) hPanIN 3. (C), Ten independent immunohistochemistry (IHC) specimens from murine and human pancreata were evaluated for CXCR4 incidence in PanIN lesions and demonstrate increased CXCR4 expression with progression from normal duct to PanIN3. The number of PanIN lesions (1A-3) that stained positive for CXCR4 was divided by the total number of each particular PanIN subtype present to obtain the % positive. The total number of PanIN examined is indicated by the number above each bar.