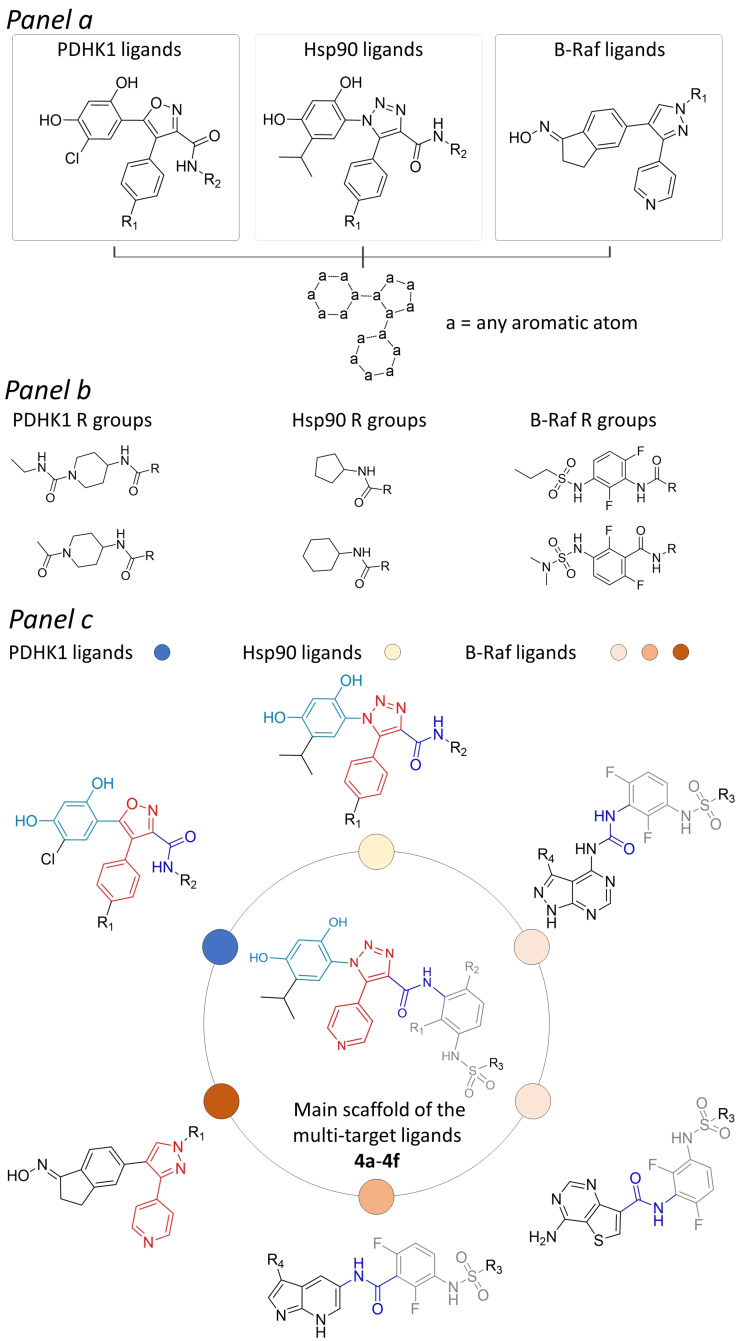
Figure 1.
Design of Hsp90 inhibitors 4 a–4 f with putative multi‐target activity. The compounds were obtained by firstly assembling selected molecular core scaffolds of known Hsp90 inhibitors (i. e., substituted resorcinol, 4‐phenyl‐1,2,3‐triazole molecules), [19] with those selected from reported PDHK1 ligands (based on substituted resorcinol, 4‐phenyl‐(1,2‐oxazole)), [28] and B‐Raf ligands (based on substituted 4‐(1H‐pyrazol‐3‐yl)pyridine) (panel a).[ 29 , 30 , 31 ] Further similarity estimations performed on selected inhibitors of these proteins allowed to identify chemical substituents conferring high potency and selectivity towards B‐Raf protein kinases,[ 30 , 31 ] which are expected to be well accepted also by Hsp90 and PDHK1. Panel b reports few among the most similar Hsp90 and PDHK1 amide substituents, identified with respect to unsubstituted (R1, R2=H) and substituted (R1, R2=F) phenyl‐3‐sulfonamides or phenyl‐3‐sulfamides chemical moieties present in the selected B‐Raf compounds. The assembled molecular core scaffold and selected substituents were finally integrated into chemical entities with the structural details potentially required to achieve efficient binding to Hsp90, B‐Raf and PDHK1 (panel c).