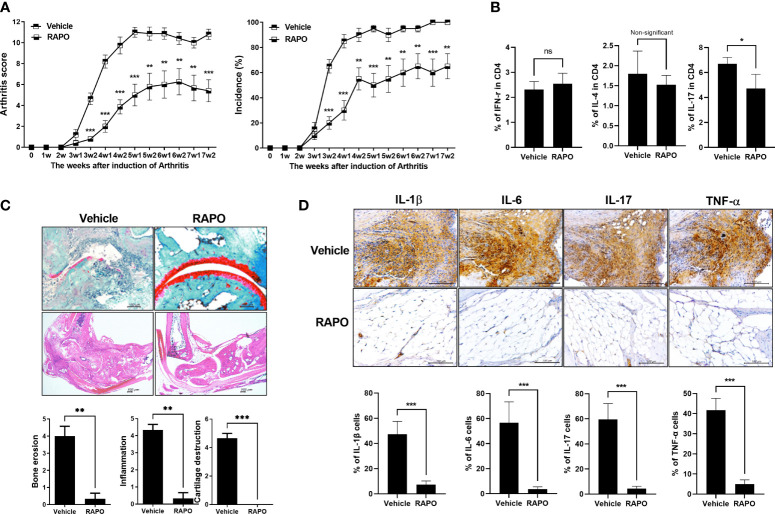
Figure 5.
Effects of Bifidobacterium longum RAPO in obese CIA mice. Mice were administered orally with B. longum RAPO (1 × 108 CFU/mouse) once daily for 7 weeks after the immunization boost. (A) Arthritis score and incidence of B. longum RAPO-treated mice compared with those of obese CIA mice (n = 5 for each group). (B) B. longum RAPO reduces IL-17 expression in CD4 T cells from the spleen of mice with obese CIA. Flow cytometry of Th1 cells (IFN-r+CD4+), Th2 cells (IL-4+CD4+), and Th17 cells (CD4+IL17+) from the spleen of mice with obese CIA. (C) Effect of B. longum RAPO on RA in mice with obese CIA. Tissue from the hind paw joints was stained with hematoxylin and eosin, as well as safranin O. (D) B. longum RAPO inhibits the proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, IL-17, and TNFα in CIA mice. Representative immunohistochemistry images showing that B. longum RAPO alleviates RA in obese CIA mice. Synovium sections treated with a vehicle, B. longum RAPO, or vehicle were stained for IL-1β, IL-6, IL-17, and TNFα. Scale bar, 100 μm. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 (vs. vehicle-treated group).