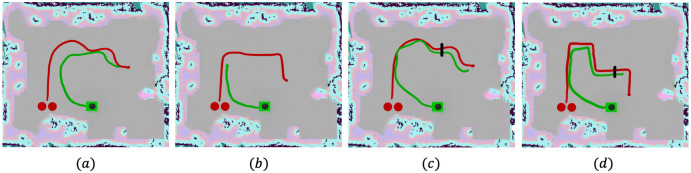
Fig 9. Improved pedestrian tracking using CCTV camera.
Trajectories of two non-compliant pedestrians (in red) and the robot pursuing them (in green) in the mapped environment shown in Fig 5c. The pink and blue colors denote the static obstacles in the environment. a. The robot only uses its RGB-D camera to track the pedestrian and pursues the pedestrians successfully when they move in a smooth trajectory. b. The robot’s RGB-D camera is unable to track the pedestrians when they make a sudden sharp turn. c. When the CCTV camera is used to track the pedestrians, the robot follows their trajectories more closely. d. Pedestrians making sharp and sudden turns can also be tracked. The black line denotes the point at which the pedestrians leave the CCTV camera’s FOV, and the RGB-D camera tracks the pedestrians from this point. Sharp turns in d again become a challenge.