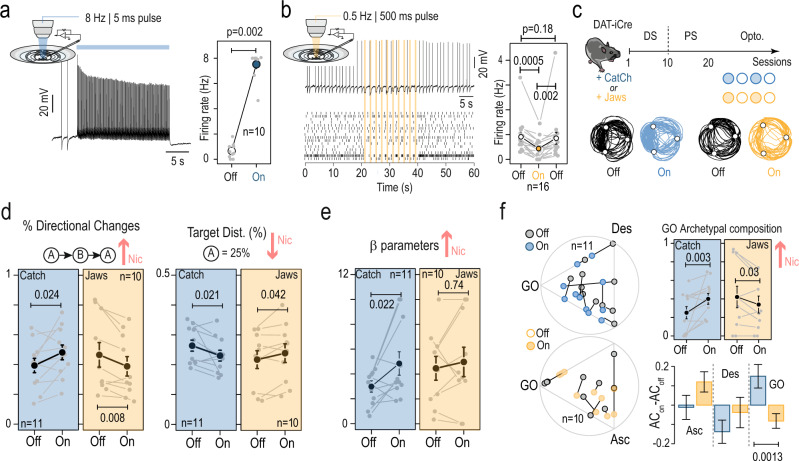
Fig. 5. Optogenetic manipulation of VTA DA neuron activity recapitulated the behavioral adaptations observed under chronic nicotine exposure.
a Left: representative ex vivo current-clamp recording of a VTA DA neuron transduced with CatCh and stimulated with 5 ms blue light pulses at 8 Hz. Right: average increase in basal firing frequency upon optogenetic stimulation for n = 10 neurons (p value = 0.002, two-sided Wilcoxon test). b Top left: representative ex vivo current-clamp recording of a VTA DA neuron transduced with Jaws and stimulated with 500 ms green light pulses at 0.5 Hz. Bottom left: raster plot for n = 16 neurons. Right: average decrease in basal firing frequency upon optogenetic stimulation, and return to the baseline after the photo-stimulation period, for n = 16 neurons (p value: ns = 0.18; **0.004; **0.0014, two-sided Wilcoxon test with Holm correction). c Task design and photo-stimulation protocols. DATiCRE mice transduced with either an AAV-DIO-CatCh-YFP in the VTA (CatCh, blue) or an AAV-DIO-Jaws-eGFP (Jaws, yellow) and were implanted unilaterally with bipolar stimulating electrodes for ICSS in the MFB (see also Supplementary Table 1). Following the deterministic (DS) and probabilistic setting (PS) sessions, they received 2 paired Off (filled circles) and Off (open circles) sessions with the same rules as in the PS. Below: representative trajectories of a CatCh and Jaws-transduced mouse with (blue and yellow) and without (black) optogenetic stimulation of VTA DA neurons. d Left: percentage of directional changes and (right) target distribution (P25) in individual mice (gray points) for CatCh (n = 11) and Jaws-transduced (n = 10) mice during On and Off sessions. Mean + sem are in black. Red arrows indicate the net effect of nicotine for comparison (one-sided Student’s t-test or Wilcoxon test). e Same as (d) for the softmax model β parameter. f Left: position of each animal in the ternary archetype plot for CatCh (n = 11, above) and Jaws-transduced (n = 10, below) mice, in On (blue or yellow points) and Off (gray point) sessions. Right: (above) GO archetypal composition in individual mice (gray points) during On and Off session, for CatCh (n = 11) and Jaws-transduced (n = 10) mouse. Mean + sem are in black; (below) net effect (ON–OFF) of light stimulation in archetypal composition for each archetype. Optogenetic activation of DA neurons triggered a shift of the behavior towards the GO phenotype while optogenetic inhibition induced a shift of the behavior away from GO (one-sided Student’s t-test). For (a, b) and (d, f), data are shown as mean ± sem. See also source data.