Figure 4. Tau-V337M organoids exhibit early neuronal maturation and upregulation of synaptic signaling pathways.
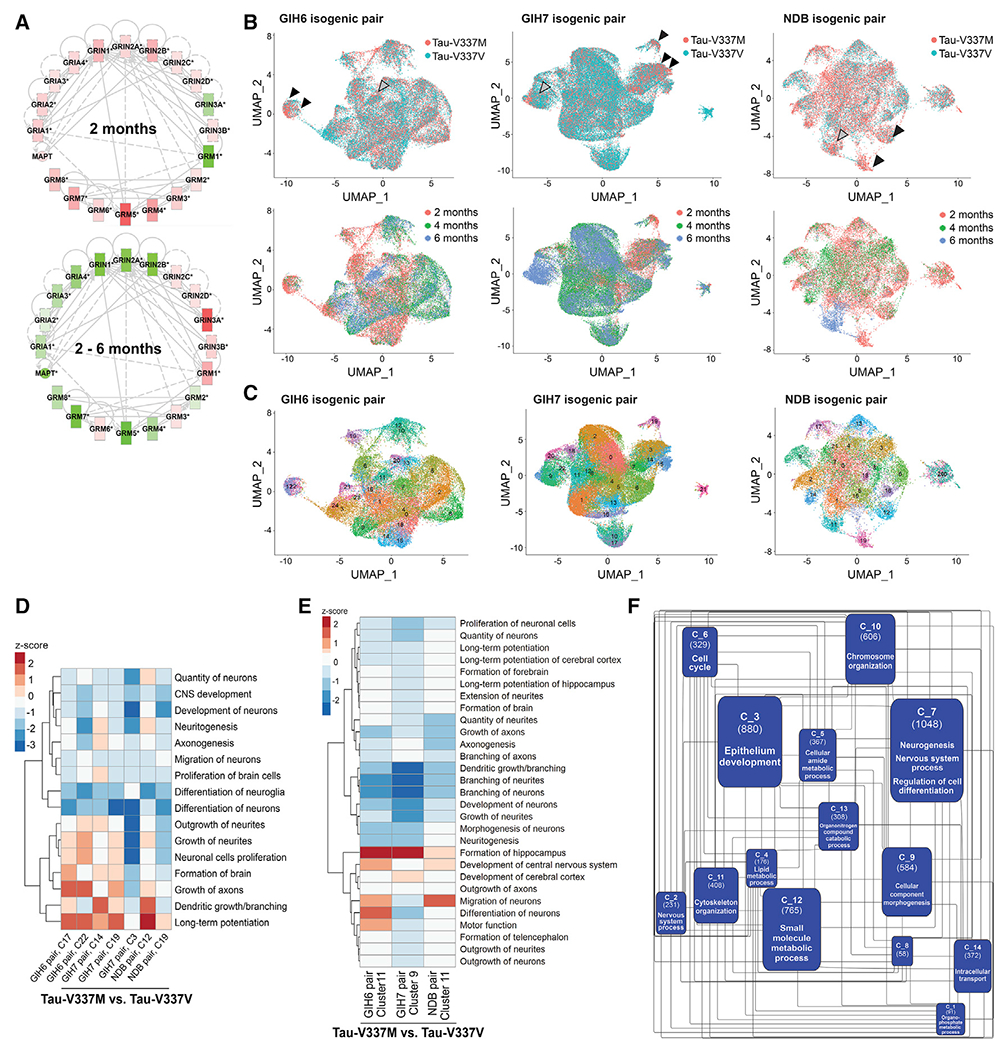
(A) Expression and connectivity of glutamatergic receptor genes and MAPT at 2 months and 2–6 months. Red, upregulation in tau-V337M organoids compared with isogenic V337V; green, downregulation; depth of color, extent of expression fold change.
(B) UMAPs of glutamatergic neurons for each isogenic pair colored by mutation (top) and age (bottom). 2-month V337M-enriched clusters are indicated by black arrowheads, and 6-month V337M-enriched clusters are indicated by gray arrowheads.
(C) UMAPs in (B) colored by Seurat cluster.
(D and E) Z scores for enriched pathways derived from IPA for V337M-enriched 2-month (D) and 6-month (E) glutamatergic neuronal clusters (C) for each isogenic pair.
(F) Network analysis constructed from significantly differentially expressed genes over time between tau-V337V and tau-V337M glutamatergic neurons following pseudobulk analysis of scRNA-seq data.
Communities (C_) are labeled with ID number in bold, with the number of genes in parentheses and the most frequent parent GO term following GO enrichment and semantic similarity analysis. See also Figures S4 and S5.
