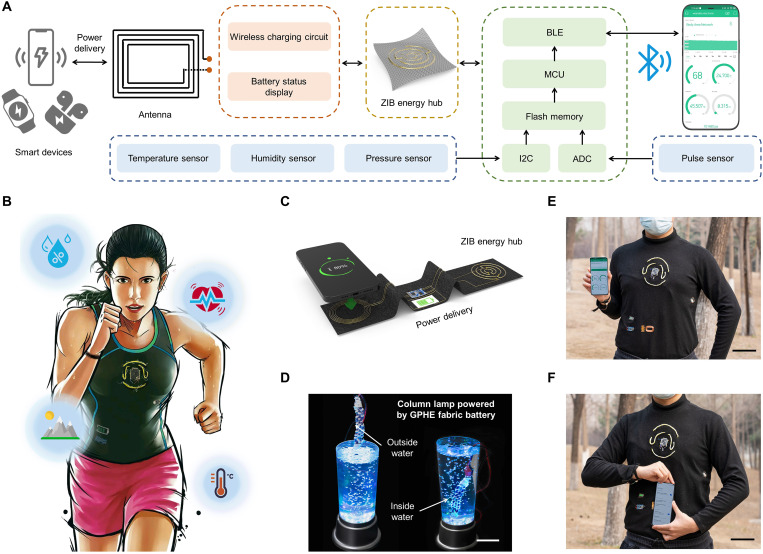
Fig. 5. Powering a TBAN.
(A) Block diagram of the wearable system of the flexible ZIB-powered TBAN. (B) Illustration of wireless TBAN powered by ZIB fibers consisting of interconnected wearable sensors on clothing. The data collected by TBAN are uploaded to the cloud by Bluetooth for real-time body-state monitoring and telemedicine care. (C) Textile-based wireless power delivery between the smart phone and ZIB fibers. Photo credit: Xiao Xiao, University of California, Los Angeles. (D) GPHE fabric ZIB maintaining stable voltage output underwater. Scale bar, 10 cm. Photo credit: Xiao Xiao, University of California, Los Angeles. (E) Photograph of the application of body-state monitoring, with a coauthor wearing the TBAN in the outdoor environment. Scale bar, 10 cm. Photo credit: Xiao Xiao, Beihang University. (F) Photograph of convenience wireless charging of the TBAN. Scale bar, 10 cm. Photo credit: Xiao Xiao, Beihang University.