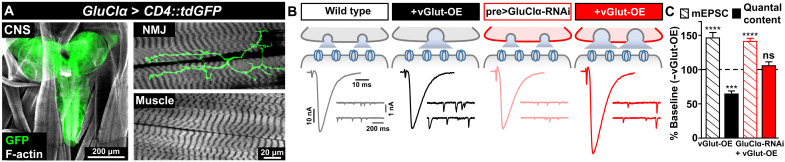
Fig. 3. GluClα is expressed in motor neurons and required presynaptically for PHD.
(A) Representative images of the larval brain [central nervous system (CNS)] and muscle 6/7 NMJ of a GFP reporter driven by the GluClα promoter (w;GluClα-Gal4/UAS-CD4::tdGFP). Immunostaining using anti-GFP and anti-phalloidin (F-actin marker) is shown. GluClα is expressed in the CNS and in motor neurons, while no signal is detected in the muscle. (B) Schematic and representative EPSC and mEPSC traces in wild type, vGlut-OE, and following knockdown of GluClα expression in motor neurons by RNAi at baseline (pre>GluClα-RNAi: w;OK371-Gal4/UAS-GluClα RNAi;UAS-Dcr2/+) and with vGlut-OE (w;OK371-Gal4/UAS-vGlut,UAS-GluClα RNAi;UAS-Dcr2/+). PHD fails to be expressed in pre>GluClα-RNAi+vGlut-OE. (C) Quantification of mEPSC and quantal content values in the indicated genotypes relative to baseline (wild type, n = 12; +vGlut-OE, n = 13; pre>GluClα-RNAi, n = 16; +vGlut-OE, n = 20). ***P < 0.001 and ****P < 0.0001.