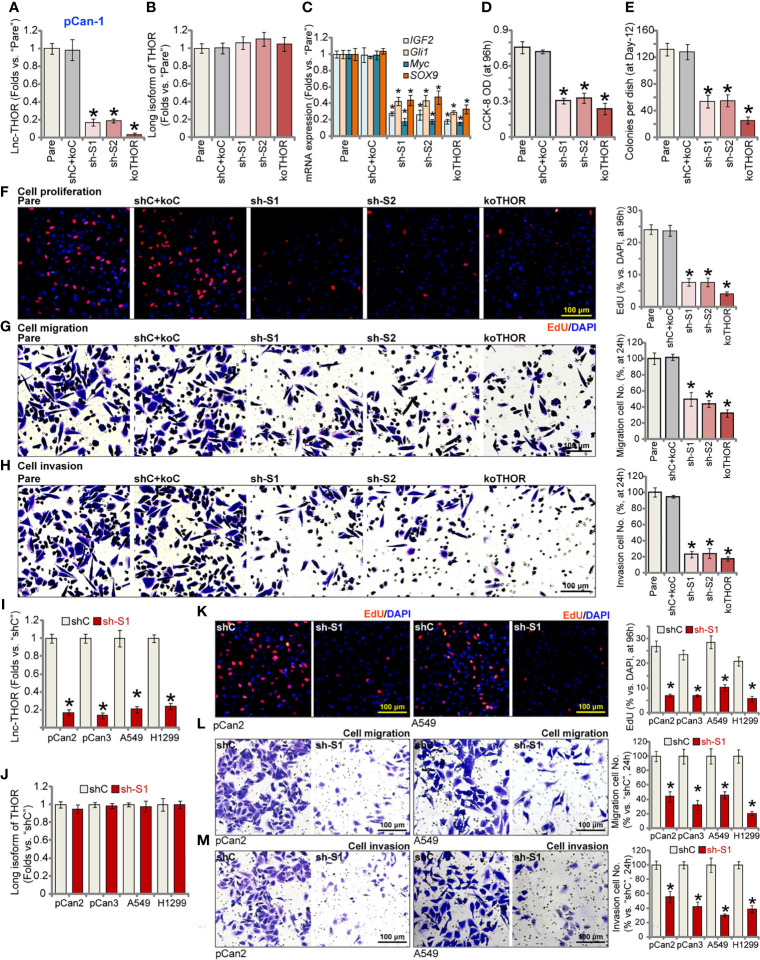
Figure 1.
Lnc-THOR shRNA or KO inhibits NSCLC cell viability, proliferation, migration and invasion. Lnc-THOR shRNA (“sh-S1” or “sh-S2”, two different sequences)-expressing pCan-1 primary NSCLC cells, the CRISPR/Cas9-edited Lnc-THOR KO pCan-1 cells (“koTHOR”), or pCan-1 cells expressing the scramble control shRNA plus the Cas9-KO empty vector (“shC+koC”), were established; Expression of Lnc-THOR (A) and listed genes (B, C) was shown; Cells were cultured for applied time periods, and cell viability (CCK-OD, D), colony formation (E), proliferation [EdU incorporation, (F)], migration and invasion [“Transwell” assays, (G, H)] were tested. Primary NSCLC cells (pCan-2 and pCan-3, derived from two different patients) or established cell lines (A549 and H1299), stably expressing the “sh-S1” Lnc-THOR shRNA or the scramble control shRNA (“shC”), were established; Expression of Lnc-THOR (I) and the long isoform of THOR (J) were shown; Cell proliferation (K), migration (L) and invasion (M) were tested similarly. For the in vitro functional assays, the exact same number of viable cells of different genetic treatments were seeded onto each well/dish (“Day-0”/0h). “Pare” stands for the parental control cells. Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD, n=5). *P < 0.05 vs. “Pare”/”shC” cells. The experiments were repeated five times, with similar results obtained. Scale Bar = 100 μm (F–H, K–M).