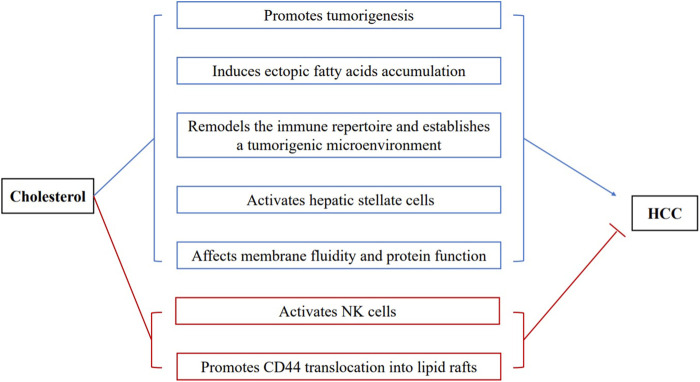
FIGURE 2.
The complex roles of cholesterol in the development of HCC. Proposed mechanisms for the pathogenic roles of cholesterol in HCC are revealed (blue characters): (1) promoting tumorigenesis; (2) inducing ectopic fatty acids accumulation; (3) remodeling the hepatic immune repertoire and establishing a tumorigenic microenvironment; (4) activating hepatic stellate cells; (5) affecting membrane fluidity and protein function. Mechanisms by which cholesterol inhibits HCC development (red characters): (1) activating NK cells to fight against hepatoma cells; (2) promoting the translocation of CD44 into lipid rafts and attenuating CD44-mediated migration and metastasis of HCC.