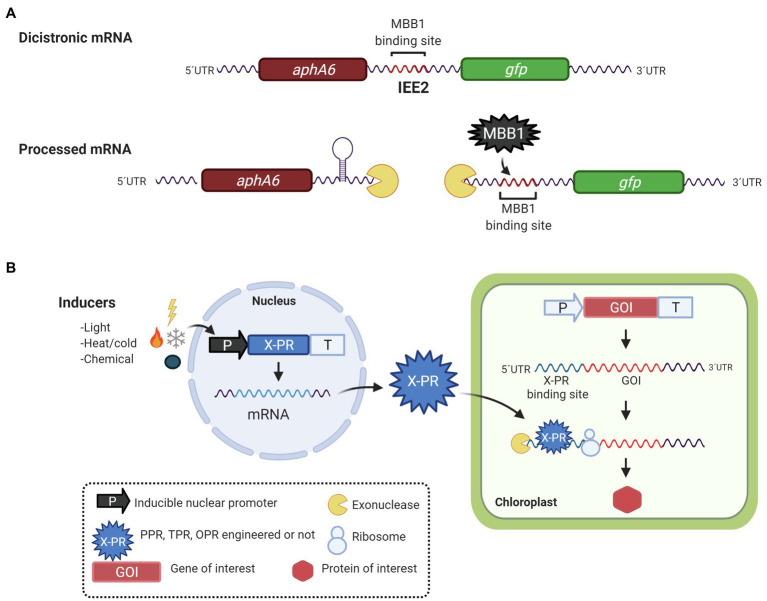
Figure 3.
Biotechnological applications of PPR, OPR, and HAT proteins. (A) Expression of synthetic operons in C. reinhardtii. Binding sites for PPR and HAT-TPR protein have been used as intercistronic expression elements (IEE) for the simultaneous expression of two or more foreign genes. In this example, the IEE2, deriving from the psbN-psbH intergenic region, contains a binding site for MBB1, a HAT-TPR protein. When IEE2 was used between two foreign genes, aphA-6 (conferring resistance to kanamycin) and gfp it was suggested that IEE2 acts as a binding site for an M factor thus stabilizing and protecting the gfp mRNA from exonuclease degradation and allowing the production of GFP protein. (B) Nuclear vector for inducible expression of chloroplast genes. The transcription of a nucleus-encoded helical repeat protein (X-PR, engineered or not) is regulated by an inducible promoter activated by light, temperature (hot or cold), or a chemical inductor. After the X-PR is translated in the cytosol, it is transported to the chloroplast where it anchors to its chloroplast mRNA target. X-PR acts then as M and/or T factor, promoting the production of the protein of interest in the chloroplast.