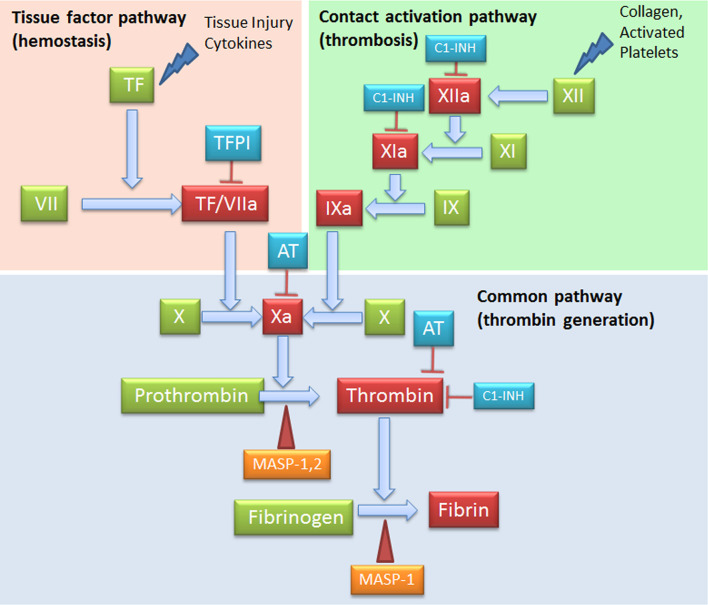
Figure 4.
Complement Components that act on the coagulation system. The intrinsic (FXII) and the extrinsic (TF/thromboplastin) pathways initiate the coagulation cascade, both converging at the common point of FX activation. FXa is causes prothrombin (FII) activation in thrombin (FIIa), which leads to the formation of fibrin from the soluble fibrinogen. MASP-1 and MASP-2 directly activate thrombin by cleaving prothrombin, and MASP-1 is able to cleave fibrinogen to generate fibrin monomers. C1-INH exerts its inhibitory activity on the coagulation system by acting on FXIIa, FXIa and thrombin. AT, Antithrombin; C1-INH, C1-inhibitor; MASP, MBL (mannose binding lectin) associated serine protease; TF, Tissue factor; TFPI, Tissue factor pathway inhibitor.