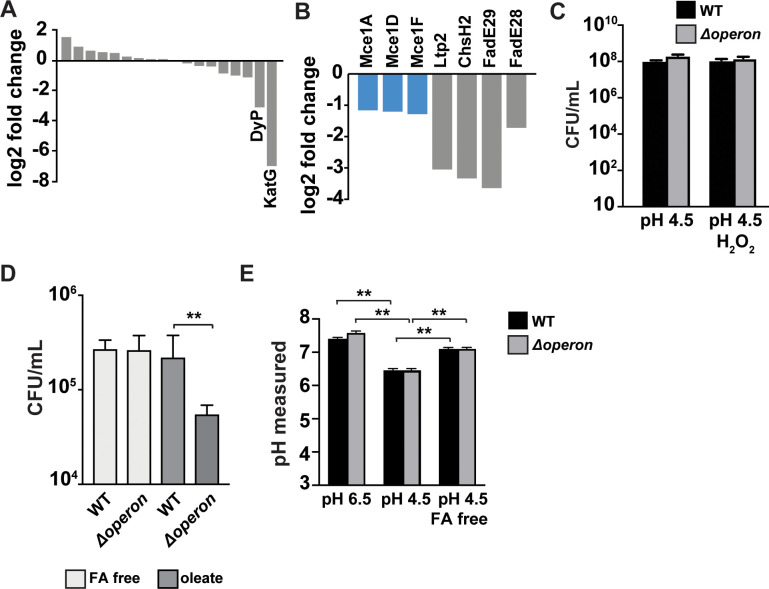
Figure 3. Susceptibility of Mtb nanocompartment mutants to oxidative and acid stress is mediated by free fatty acids.
(A) Transposon sequencing (Tn-seq) data showing normalized sequence reads per gene for all putative Mtb peroxidases, catalases, and superoxide dismutases and (B) lipid and cholesterol metabolism Mtb mutants that were significantly attenuated following 72 hr exposure to 2.5 mM H2O2 at pH 4.5. (C) CFU enumeration of wild-type Mtb and Δoperon mutants following 24 hr exposure to 2.5 mM H2O2 at pH 4.5 in Sauton’s minimal medium and (D) 72 hr exposure to 2.5 mM H2O2 at pH 4.5 in 7H9 medium prepared using fatty acid (FA)-free bovine serum albumin (BSA) ± oleic acid (150 µM). (E) Intrabacterial pH measurements of wild-type and Δoperon Mtb expressing pUV15-pHGFP following 20 min exposure to 5 mM H2O2 at pH 6.5 or pH 4.5. 7H9 medium was prepared with standard BSA or FA-free BSA. Figures are representative of at least two (D) or three (A–C, E) independent experiments. p-Values were determined using an unpaired t-test. *p<0.05, **p<0.01.