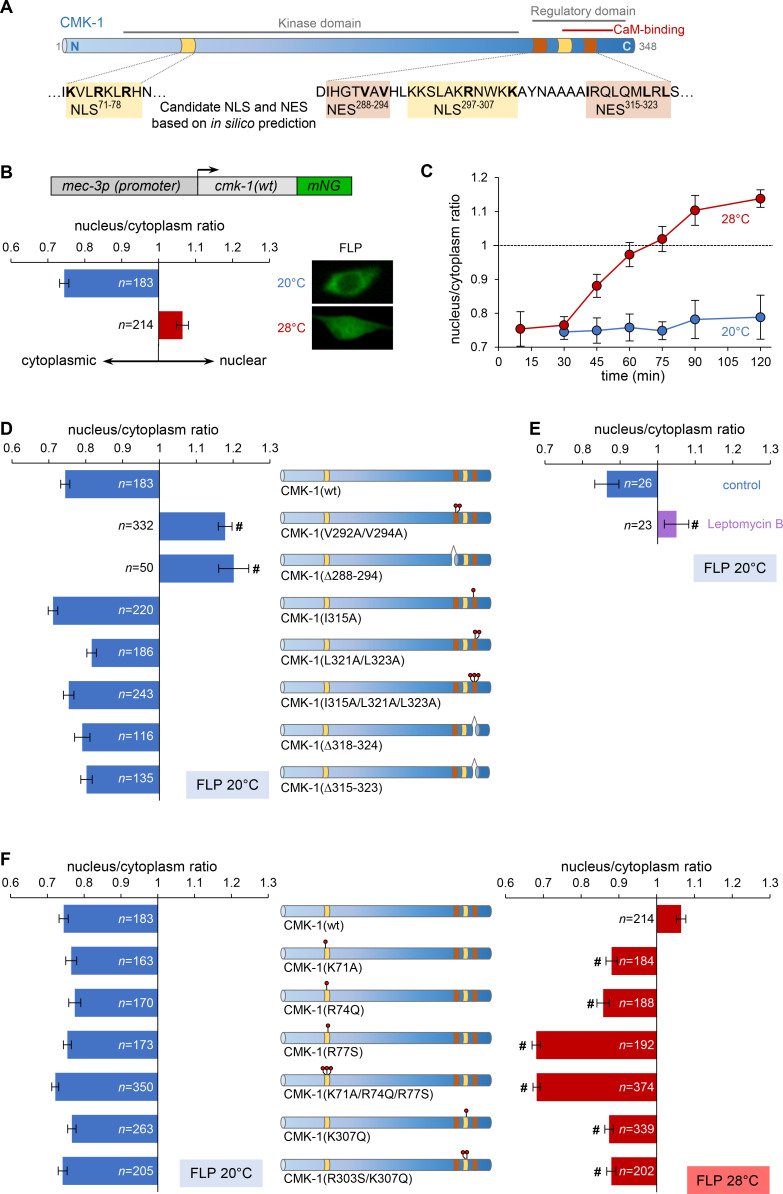
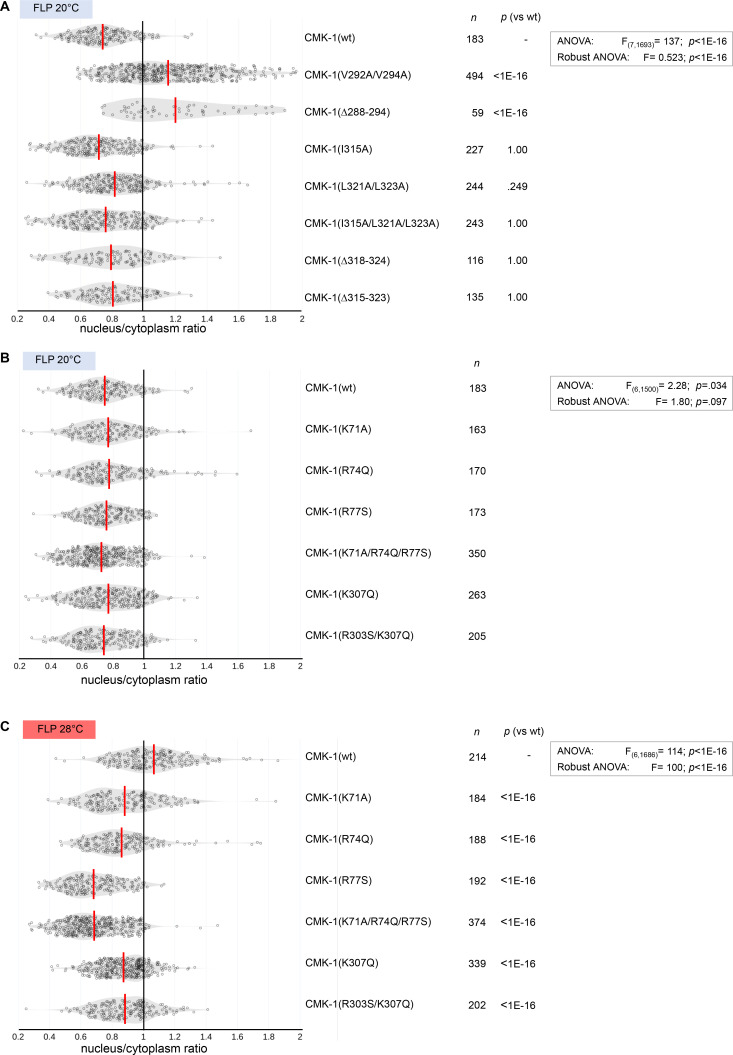
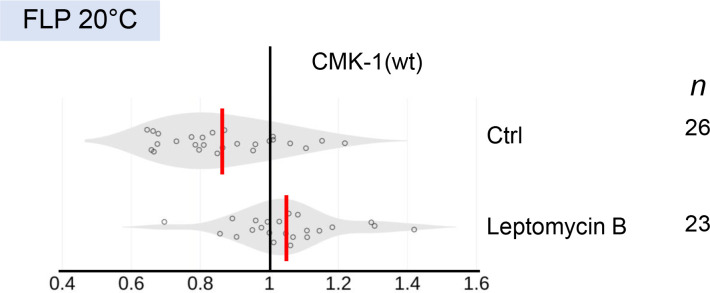
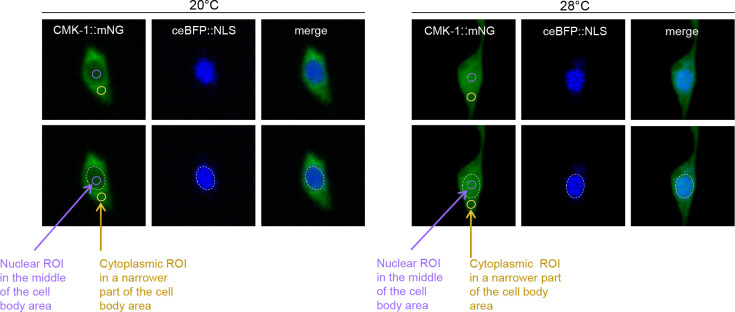
Figure 1. Specific nuclear export sequence (NES) and nuclear localization signal (NLS) control CMK-1 localization in response to temperature in FLP.
(A) Schematic of CMK-1 topology highlighting the localization of in silico-predicted NES and NLS and their sequence. (B) Subcellular localization of CMK-1(wt)::mNeonGreen (mNG) reporter expressed in FLP via the depicted transgene (top). Average nuclear/cytoplasm fluorescent signal ratio (± SEM, left) and representative confocal micrographs (right) showing heat-evoked nuclear translocation of wild-type CMK-1 in young adult FLP neurons after 90 min at 28°C as compared to control at 20°C. (C) Kinetics of CMK-1::mNG nuclear accumulation. Data as nuclear/cytoplasmic fluorescent signal ratio average (± SEM). (D, E) Subcellular localization of CMK-1::mNG reporters carrying the depicted mutations in candidate NES (D), as well as following 90 min incubation with 50 µM leptomycin B or vehicle control (E). Data as nuclear/cytoplasmic signal ratio average (± SEM). (F) Same as for panel (D), but with mutations in the depicted candidate NLS in animals incubated 90 min at 20°C (blue, left panel) or 90 min at 28°C (red, right panel). #p<0.001 versus CMK-1(wt) by Bonferroni contrasts. The number of animals scored in each condition is indicated in the figure (n). Experiments reported in panels (B), (D), and (F) were run in parallel and the CMK-1(wt) dataset is common across these panels.