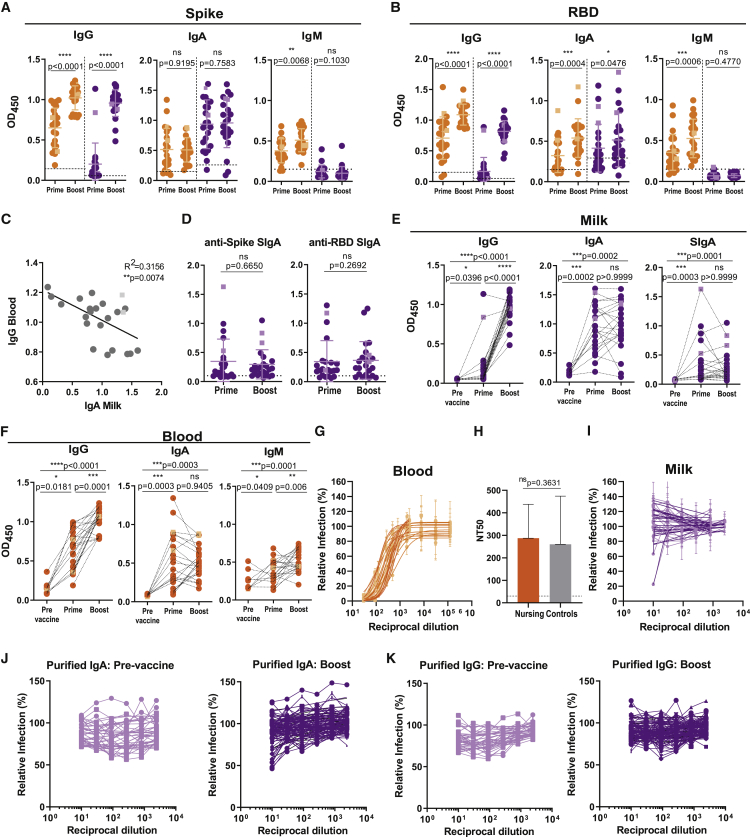
Figure 2.
Neutralizing antibodies are found in blood and less frequently in milk after second vaccine dose
(A) Anti-spike IgG, IgA, and IgM at ∼10 days after first (prime) and second (boost) vaccine doses in plasma and in skim milk, measured by absorbance at 450 nm (OD450).
(B) Anti-RBD IgG, IgA, and IgM performed as in (A).
(C) Correlation between anti-spike IgA in skim milk versus anti-spike IgG in the blood.
(D) Comparison between anti-spike- and anti-RBD SIgA at ∼10 days after first (prime) and second (boost) vaccine doses, measured as in (A).
(E) Donor-matched analysis of anti-spike IgG, IgA, and SIgA, pre-vaccination and after first (prime) and second (boost) vaccine doses, in skim milk.
(F) Donor-matched analysis of anti-spike IgG, IgA, and IgM, pre-vaccination and after first (prime) and second (boost) vaccine doses, in blood.
(G) Plasma neutralization curves.
(H) Plasma neutralization titers (NT50) in nursing and control women.
(I) Skim milk neutralization curves.
(J) Neutralization curves for skim milk purified IgA concentrated 5-fold, pre-vaccination and ∼10 days after vaccine boost.
(K) Neutralization curves for skim milk purified IgG concentrated 5-fold, pre-vaccination and ∼10 days after vaccine boost.
Orange, plasma; purple, skim milk. Circles, Pfizer; squares, Moderna. Dashed line, assay cutoff. n = 23 nursing women and n = 22 controls. p values determined using parametric paired t test and non-parametric paired Wilcoxon test as appropriate and using ANOVA, post hoc Holm-Sidak and Kruskal-Wallis tests, and post hoc Dunn test when comparing three groups. Spearman correlation. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; ns, not significant.