Figure 2.
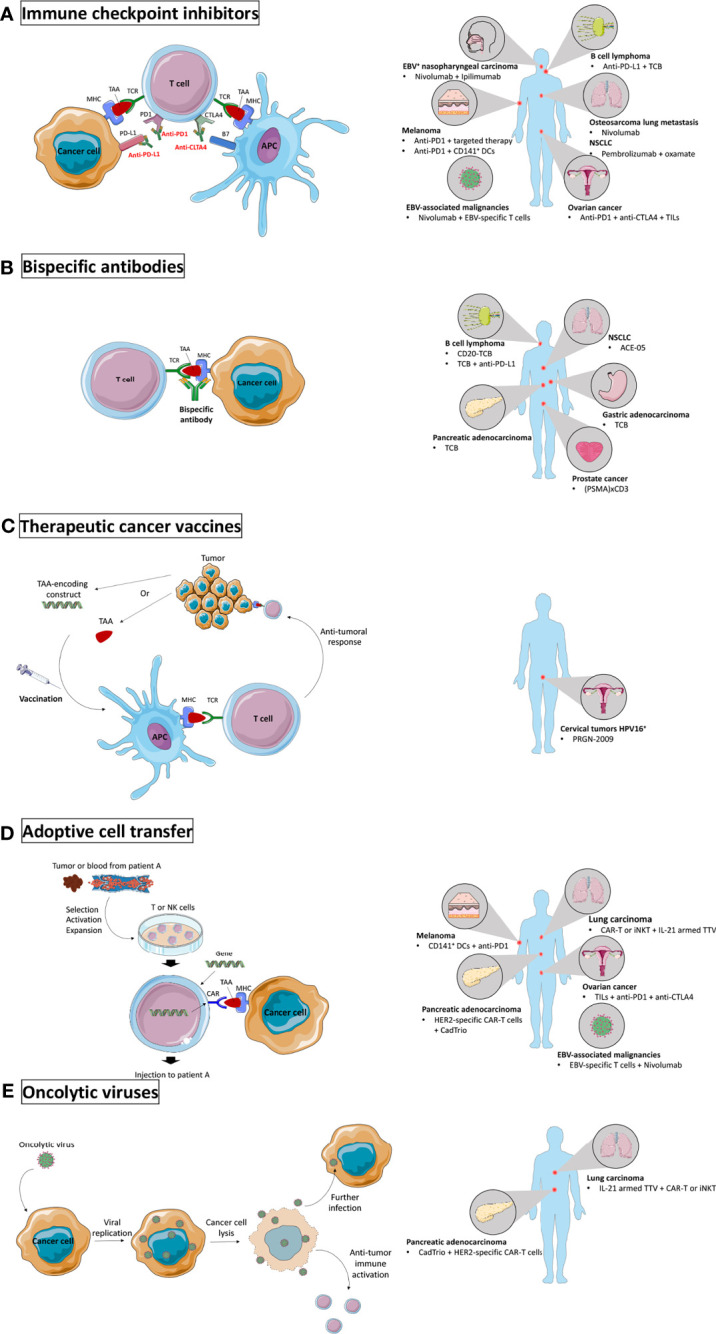
Novel immunotherapy settings tested in humanized mice. (A) Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) prevent engagement of inhibitory receptors and allow activation of anti-tumoral immune activity. ICI were tested in humanized mice to target EBV+ nasopharyngeal carcinoma and other EBV-associated malignancies, melanoma, B cell lymphoma, osteosarcoma lung metastases, non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC), and ovarian cancer. (B) Bispecific antibodies form a bridge between two target cells and were tested in humanized mice to target B cell lymphoma, pancreatic adenocarcinoma, NSCLC, gastric adenocarcinoma, and prostate cancer. (C) Therapeutic cancer vaccines boost the anti-tumor activity by injecting TAAs or TAA-encoding constructs to the patient. They were tested in humanized mice to target HPV16+ cervical tumors. (D) Adoptive transfer of ex vivo modified immune cells to improve their anti-tumor activity has been tested in humanized mice to target melanoma, pancreatic adenocarcinoma, lung carcinoma, ovarian cancer, and EBV-associated malignancies. (E) Oncolytic viruses specifically infect cancer cells and induce immunogenic cell death. They were tested in humanized mice to target pancreatic adenocarcinoma and lung carcinoma. Major histocompatibility complex (MHC); tumor associated antigen (TAA); T cell receptor (TCR); antigen presenting cell (APC); programmed cell death 1 (PD1); programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1); cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA4); Epstein-Barr virus (EBV); cluster of differentiation (CD); dendritic cells (DCs); T cell bispecific (TCB); tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs); prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA); human papillomavirus (HPV); natural killer (NK); chimeric antigen receptor (CAR); human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2); invariant natural killer T (iNKT); interleukin (IL); Torque Teno virus (TTV).
