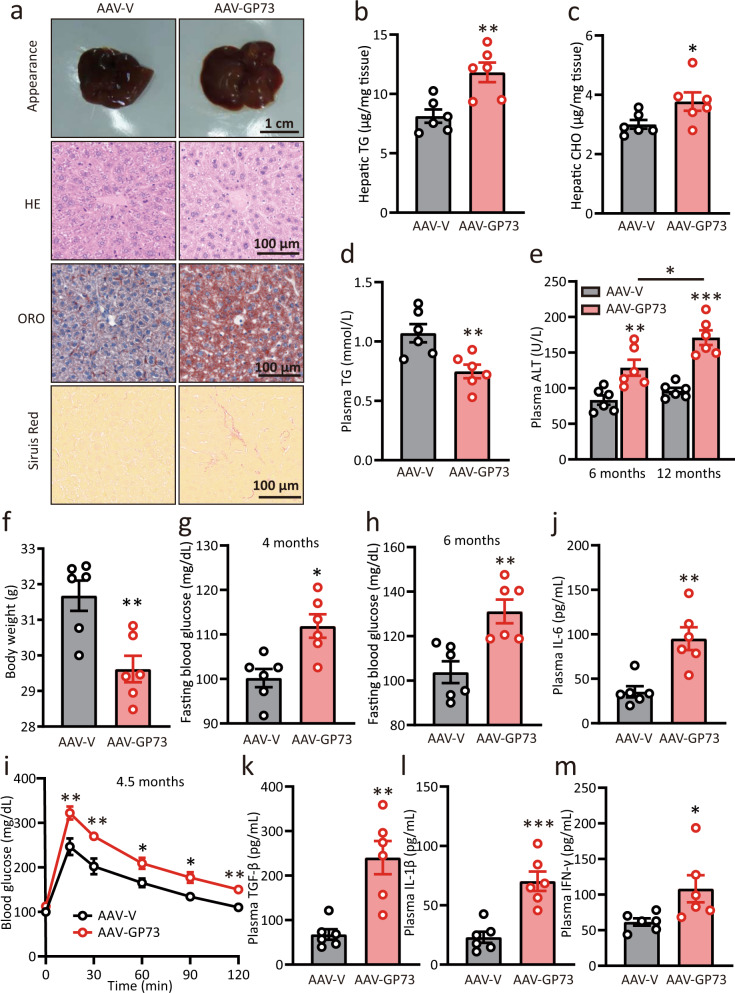
Fig. 2. Chronic elevations in hepatocyte GP73 trigger non-obese NAFLD.
a Appearance, hematoxylin–eosin (HE), Oil Red O (ORO), and Sirius red staining of liver tissues from AAV-V- or AAV-GP73 (3 × 1011 vg)-injected mice fed a regular diet for 6 months. Data were repeated three times with similar results. b–f Hepatic levels of TGs (b) and CHO (c); plasma levels of TGs (d) and ALT (e); body weights (f) of mice injected with AAV-V or AAV-GP73 and fed a regular diet for 6 or 12 months (n = 6 per group). Differences between the two groups were evaluated using two-tailed Student’s t-test. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. g, h Glucose levels in blood samples of 6 h-fasted AAV-V- or AAV-GP73-injected mice at 4 (g) and 6 (h) months after injection (n = 6 per group). Differences between the two groups were evaluated using two-tailed Student’s t-test. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. i Glucose tolerance test (GTT) results for AAV-V- or AAV-GP73-injected mice at 4.5 months after injection (n = 6 per group). Differences between the two groups were evaluated using two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni’s post hoc analysis. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. j–m Plasma levels of IL-6 (j), TGF-β (k), IL-1β (l), and IFN-γ (m) in AAV-V- or AAV-GP73-injected mice at 5 months after injection (n = 6 per group). Differences between the two groups were evaluated using two-tailed Student’s t-test. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.