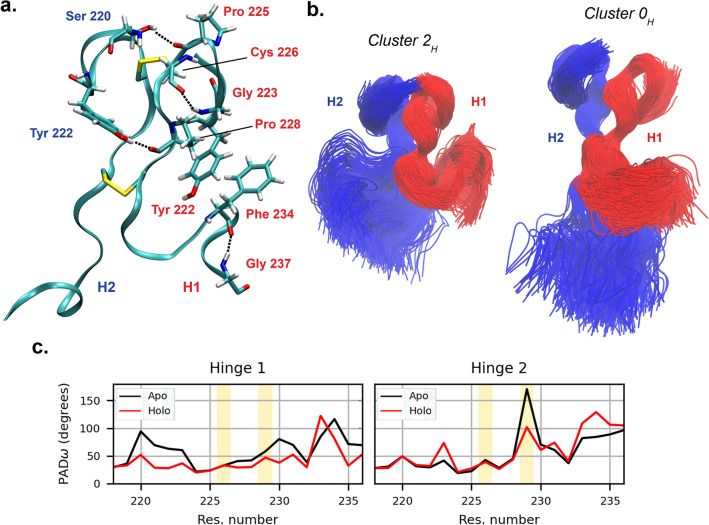
Figure 3.
(a) Interaction stabilizing the hinge conformation; residues belonging to hinge 1 are labelled in red, while those belonging to hinge 2 are in blue. The disulfide bonds between the two CYS of chains B and D, and the CYS of chains B and D, are also shown. (b) Conformational ensembles of the hinge in its most compact and most extended conformations (clusters and respectively), after structural alignment on the cysteine residues. Chain B is represented in red, chain D in blue. The overall hinge shape is determined by the conformation of H2. (c) Per-residue flexibility of hinge backbone, as quantified by PAD parameter. The yellow-shaded areas correspond to the cysteine residues forming inter-chain disulfide bonds. Particularly high is the backbone plasticity of the second cysteine in the hinge 2 of the apo antibody, which might result from the torsional stress imposed by the high conformational variability of the Fc relative to the Fab in the apo simulations.