Figure 4. Voluntary alcohol drinking sensitizes male and female CRF1+ neurons to the effects of CRF.
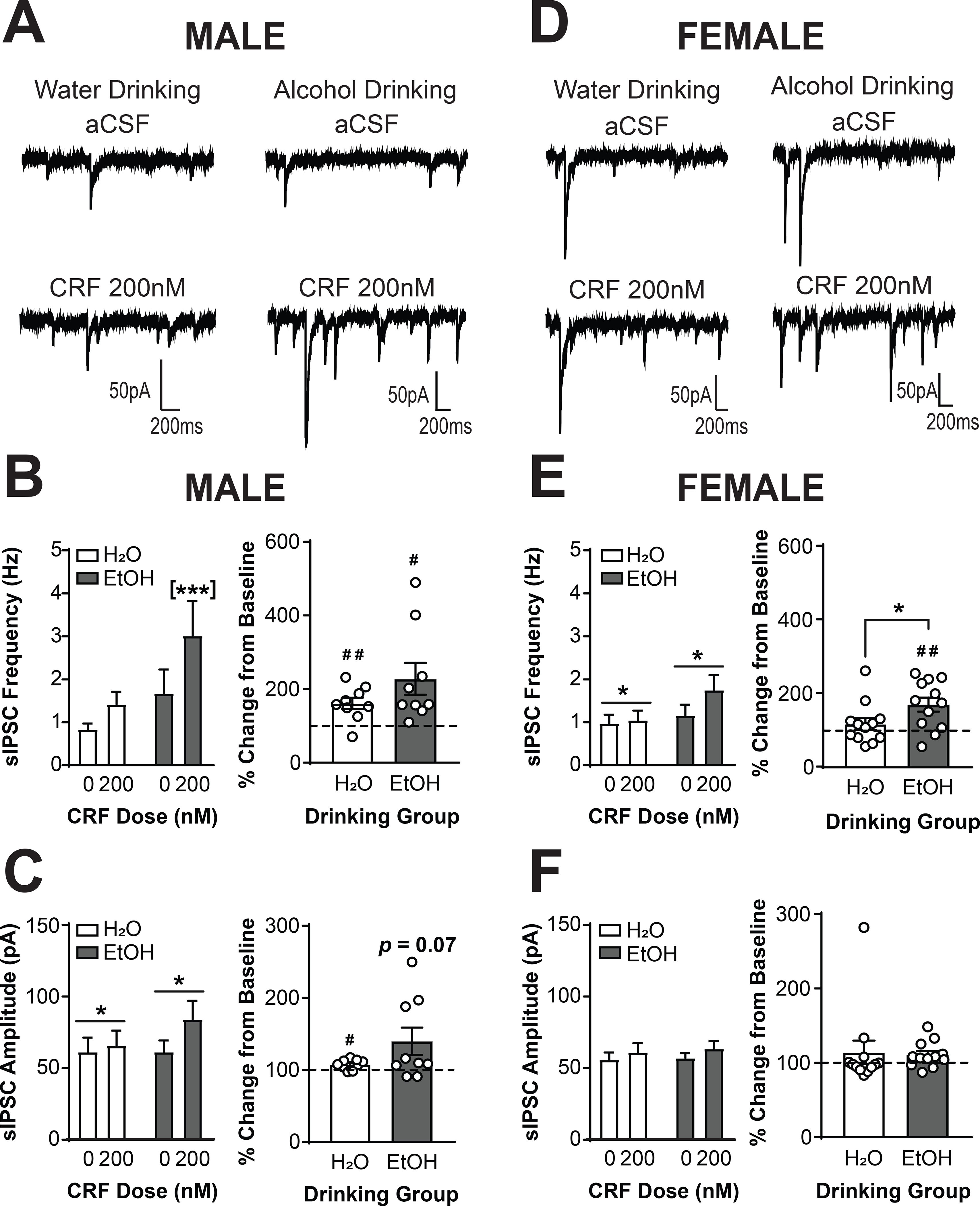
(A) Representative traces of sIPSCs in CRF1+ neurons from male mice drinking water (left) or alcohol (right) during superfusion of aCSF (top) or CRF (200 nM; bottom). (B) Summary of the effects of CRF on sIPSC frequency (left) and effects of CRF normalized into percent change from baseline (right). CRF1+ neurons from alcohol drinking mice exhibited a significant increase in sIPSC frequency whereas CRF1+ neurons from water drinking mice did not ([***]p < 0.001 by Sidak’s multiple comparisons test). When data were transformed into percent change from baseline, CRF1+ neurons from water and alcohol drinking mice demonstrated an increase in frequency from baseline (#p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 by one-sample t-test). (C) Summary of the effects of CRF on sIPSC amplitude (left) and effects of CRF normalized into percent change from baseline (right). Focal application of CRF enhanced sIPSC amplitude in male CRF1+ neurons (*p < 0.05 by two-way RM ANOVA). CRF1+ neurons from water drinking mice demonstrated a significant increase from baseline (#p < 0.05 by one-sample t-test). CRF1+ neurons from alcohol drinking mice demonstrated a trend for an increase from baseline (p = 0.07 by one-sample t-test). (D) Representative traces of sIPSCs in CRF1+ neurons from female mice drinking water (left) or alcohol (right) during superfusion of aCSF (top) or CRF (200 nM; bottom). (E) Summary of the effects of CRF on sIPSC frequency (left) and effects of CRF normalized into percent change from baseline (right). Focal application of CRF enhanced sIPSC frequency in female CRF1+ neurons in both drinking groups (*p < 0.05 by two-way RM ANOVA). However, when data were transformed into percent change from baseline, a significant difference between drinking groups emerged (*p < 0.05 by two-tailed t-test). CRF1+ neurons from water drinking mice were insensitive to focal application of CRF whereas CRF1+ neurons from alcohol drinking mice exhibited a significant increase in sIPSC frequency from baseline (##p < 0.01 by one-sample t-test). (F) Summary of the effects of CRF on sIPSC amplitude (left) and effects represented as percent change from baseline (right). sIPSC amplitude was not affected by CRF superfusion in female water or alcohol drinking mice.
