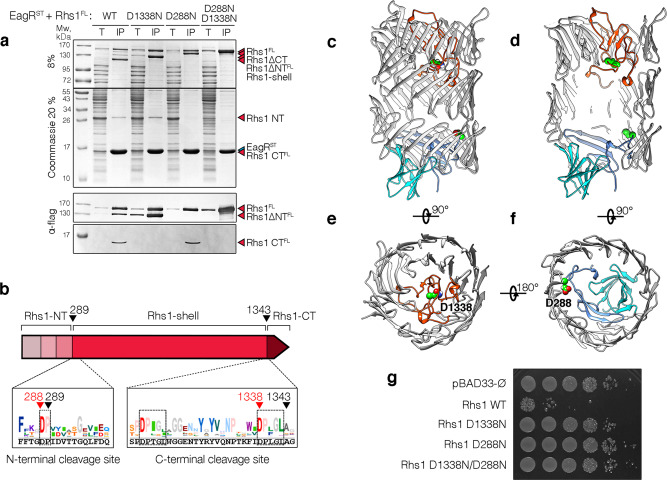
Fig. 4. N- and C-terminal autocleavages of Photorhabdus laumondii Rhs1.
a Pull-down assays. Total cell extracts (T) from E. coli BL21(DE3) cells producing Strep-tagged EagR (STEagR) and the indicated D288N, D1338N and double D288N-D1338N FLAG-tagged Rhs1 (Rhs1FL) variants were subjected to purification on streptactin-agarose beads. Strep-tagged and co-precipitated proteins were eluted with desthiobiotin (IP). Total and IP fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and co-purified proteins were stained by Coomassie blue (upper panels) or immunodetected using anti-FLAG antibodies (lower panels). The Rhs1 fragments (Rhs1ΔCT, Rhs1ΔNT, Rhs1CT and Rhs1ΔNTΔCT) are indicated on right. Molecular weight markers (Mw, in kDa) are indicated on the left. Pull-down assays have been performed at least in triplicate, and a representative experiment is shown. b Schematic representation of the Rhs1 protein highlighting the different domains and the sequence conservation of N- and C-terminal cleavage sites (logos). The sequences corresponding to the P. laumondii Rhs1 protein are shown in black, below the logos. Black arrows indicate the cleavage sites, red arrows indicate catalytic amino acid residues implicated in cleavage. c–f Position of the cleavage sites on the Rhs1 cryo-EM structure. The N- and C-terminal plugs are shown in blue and red, respectively. The aspartate catalytic residues are indicated and shown in green balls. g Toxicity assays. Serial dilutions (100–10−5) of normalized cultures of E. coli K-12 DH5α cells carrying the empty pBAD33 vector, or pBAD33 vectors producing the full-length P. laumondii Rhs1 protein (Rhs1 WT) or substitution in the aspartyl catalytic residues abolishing the N-terminal (D288N), C-terminal (D1338N) or both N- and C-terminal (D1338N/D288N) cleavages were spotted on LB agar plates supplemented with 1% glucose. Toxicity assays were done in triplicate, and a representative experiment is shown.