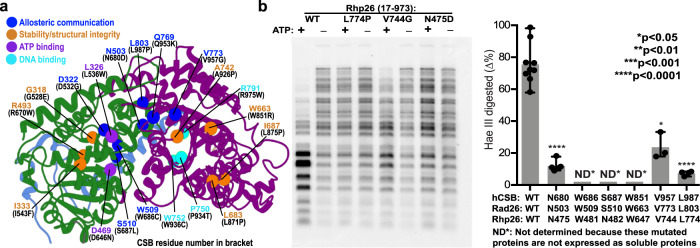
Fig. 6. Cockayne syndrome disease mutations occupy distinct positions in the Rad26 dynamic network.
a Cockayne syndrome missense disease mutations (sphere) mapped onto Rad26 and classified by type of structural or dynamic disruption they induce. Mutations are shown as disrupting allosteric communication/dynamic coupling (blue), the structural integrity or residue packing within the ATPase domains cores (orange); ATP binding (purple); DNA binding (cyan). The yeast Rad26 residues are labeled in blue while the residue numbering in human CSB sequence is shown in black in parentheses. Rad26 dynamic communities are colored in green, purple, and light blue. b In vitro DNA translocase activities of S. pombe CSB ortholog Rph26 mutated proteins measured by a chromatin remodeling assay. The Rhp26 remodeling activity is characterized by analyzing the pattern changes of the restriction enzyme HaeIII cleavage in nucleosomes assembled on a 3 kbp plasmid DNA. The three mutations at positions corresponding to CS disease mutants in the human CSB sequence dramatically reduce chromatin remodeling activity. Quantitation of enzyme activities are shown in the right panel. The experiments were repeated at least three times independently with similar results. Mean values and standard deviations are shown as column bars. p-values were calculated using Two-tailed Student’s t test (p-values N475D/4.89E−08, V744G/0.0297 and L774P/5.46E−07, respectively). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.